Introduction to Software Development
Overview of Web and Cloud Development
Cloud Applications
-
Built to work seamlessly with a Cloud-based back-end infrastructure
-
Cloud-based data storage and data processing, and other Cloud services, making them scalable and resilient
Building websites and cloud applications:
The environment is divided into two primary areas:
- Front-End
- Deals with everything that happens at the client-side
- Specializes in front-end coding, using HTML, CSS, JavaScript and related frameworks, libraries, and tools
- Back-End
- Deals with the server before the code and data are sent to the client
- Handles the logic and functionality and the authentication processes that keep data secure
- Back-end developers may also work with relational or NoSQL databases
Full-stack developers have skills, knowledge, and experience in both front-end and back-end environments.
Developers Tools:
- Code editor
- IDE
Learning Front-End Development
-
HTML is used to create the structure and CSS is used to design it and make it appealing
-
CSS is also used to create websites that have cross browser compatibility such as PC, mobiles devices etc.
-
JS adds interactivity
A front-end development language is Syntactically Awesome Style Sheets (SASS)
-
An extension of CSS that is compatible with all versions of CSS.
-
SASS enables you to use things like variables, nested rules, inline imports to keep things organized.
-
SASS allows you to create style sheets faster and more easily.
Learner Style Sheets (LESS)
-
LESSenhances CSS, adding more styles and functions. -
It is backwards compatible with CSS.
-
Less.js is a JS tool that converts the
LESSstyles to CSS styles.Websites are designed as reactive and responsive
-
Reactive or adaptive websites display the version of the website designed for a specific screen size.
-
A website can provide more information if opened on a PC than when opened on a mobile device.
-
Responsive design of a website means that it will automatically resize to the device.
-
If you open up a products’ website on your mobile device, it will adapt itself to the small size of the screen and still show you all the features.
JavaScript’s frameworksorks:
Angular Framework:
-
an open-source framework maintained by google
-
Allows websites to render HTML pages quickly and efficiently
-
Tools for routing and form validation
React.js:
-
Developed and maintained by Meta
-
It is a JS library that builds and renders components for a web page
-
Routing is not a part of this framework and will need to be added using a third-party tool
Vue.js:
-
maintained by the community and its main focus is the view layer which includes UI, buttons, visual components
-
Flexible, scalable, and integrates well with other frameworks
-
Very adaptable – it can be a library, or it can be the framework
The task of a front-end developer evolves continuously.
-
The technologies are upgraded constantly, and so the front-end developers need to keep upgrading the websites that they create.
-
The websites that they create should work in multiple browsers, multiple operating systems, and multiple devices.
The importance of Back-End Development
-
Creates and manages resources needed to respond to client requests
-
Enables server infrastructure to process request, supply data and provide other services securely
What does the back-end developer do?
-
Process the data you enter while browsing, such as:
- Login information
- Product searches
- Payment information
-
Write and maintain the parts of the application that process the inputs
Back-End Developer skills:
Examples of tasks and associated skills that back-end developers need:
APIs, routing, and endpoints:
- APIs, routes, and endpoints process requests from the Front-End
- API is a code that works with data
- Routes is a path to a website or page
- Endpoint can be an API or route
- Back-end developers create routes to direct requests to correct service
- APIs provide a way for Cloud Apps to access resources from the back-end
Back-end languages and frameworks:
Some popular back-end languages are:
- JavaScript
- Node.js
- Express
- Python
- Django
- Flask
Working with databases:
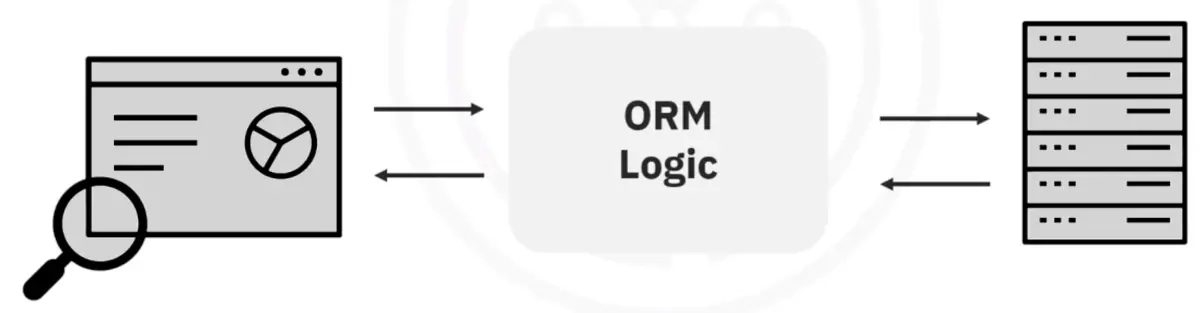
Languages and tools for working with databases:
- Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Object-Relational Mapping (ORM)
Introducing Application Development Tools
A cloud application developer’s workbench includes:
- Version Control
- Libraries
- Collection of reusable code
- Multiple code libs can be integrated into a project
- Call from your code when required
- Used to solve a specific problem or add a specific feature
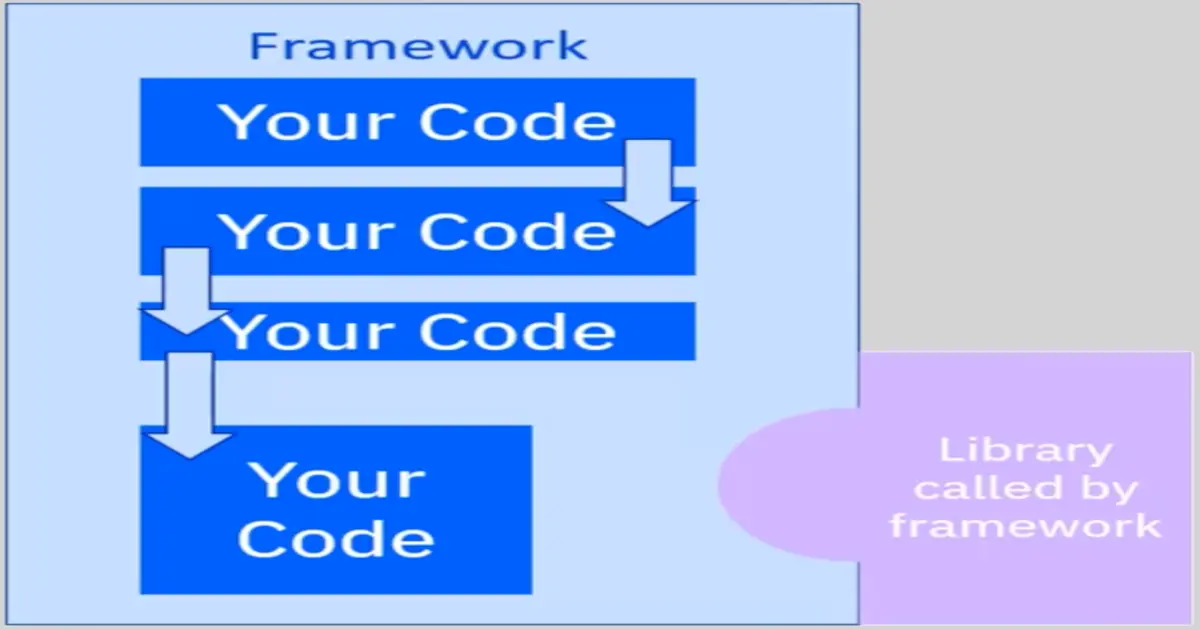
Frameworks:
-
Provide a standard way to build and deploy applications
-
Act as a skeleton you extend by adding your own code
-
Dictate the architecture of the app
-
Call your code
-
Allow you less control than libs
Inversion of Control:
-
Libs allow you to call functions as when required
-
Frameworks define the workflow that you must follow
-
Inversion of control makes the framework extensible
More tools:
-
CI/CD
-
Build tools
- Transform source code into binaries for installation
- Important in environments with many interconnected projects and multiple developers
- Automate tasks like
- Downloading dependencies
- Compiling source code into binary code
- Packaging that binary code
- Running Tests
- Deployment to production systems
Examples of Build Tools:
Packages:
- Packages make apps easy to install
- Packages contain
- App files
- Instructions for installation
- Metadata
Package managers:
- Make working with packages easier
- Coordinate with file archives to extract package archives
- Verify checksums and digital certificates to ensure the integrity and authenticity of the package
- Locate, download, install, or update existing software from a software repository
- Manage dependencies to ensure a package is installed with all packages it requires
Package Managers by platform:
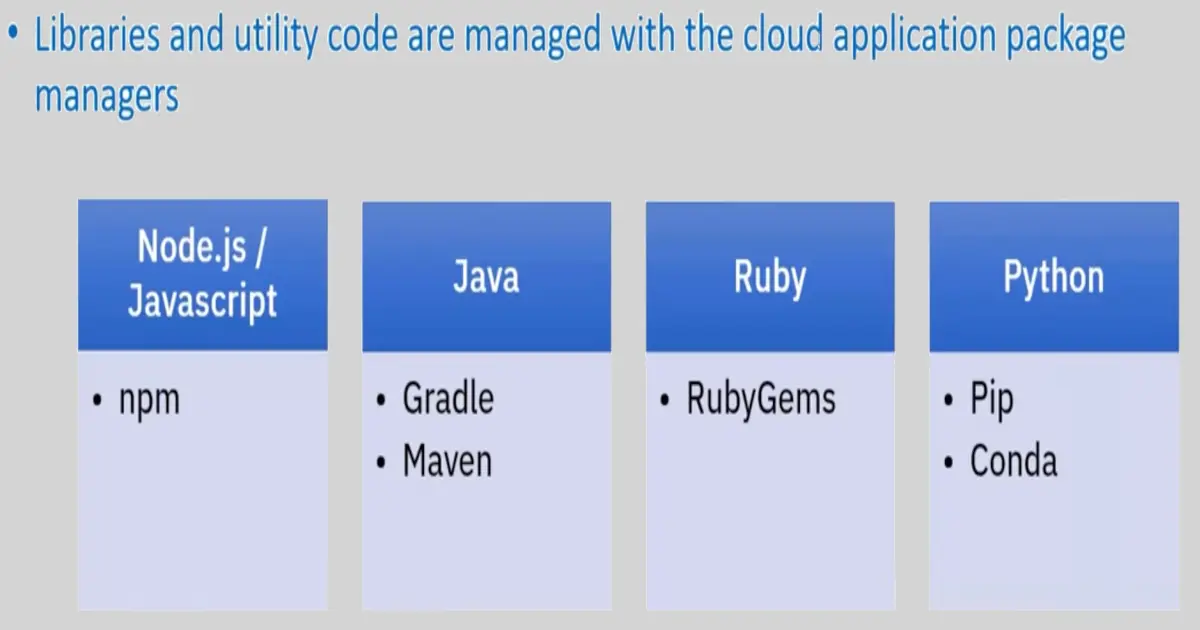
Cloud application package managers:
Introduction to Software Stacks
What is a software stack?
-
Combination of technologies
-
Used for creating applications and solutions
-
Stacked in a hierarchy to support the application from user to computer hardware
-
Typically include;
- Front-end technologies
- Back-end technologies
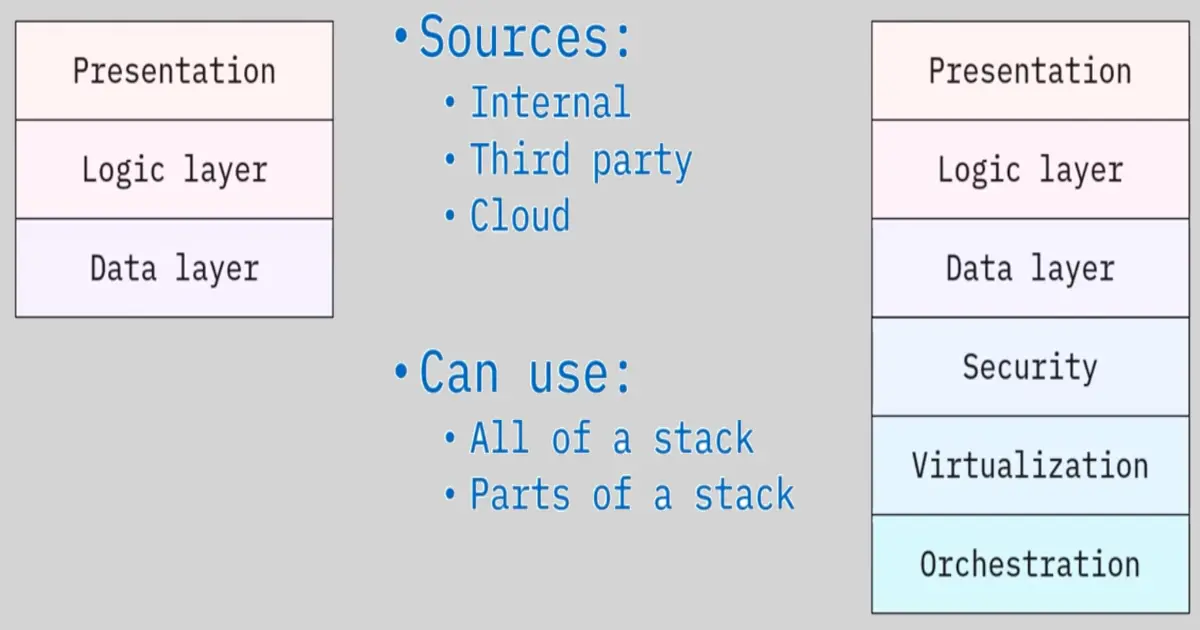
Parts of the software stack:
Examples of software stack:
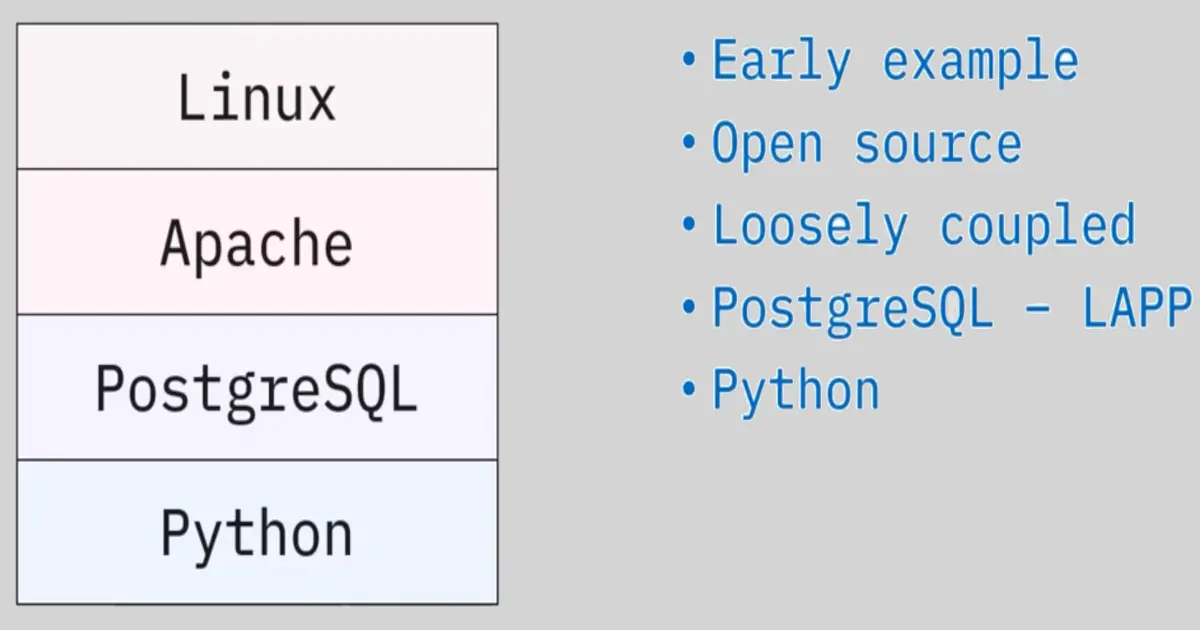
-
Python-Django
-
Ruby on Rails
-
ASP .NET
-
LAMP
-
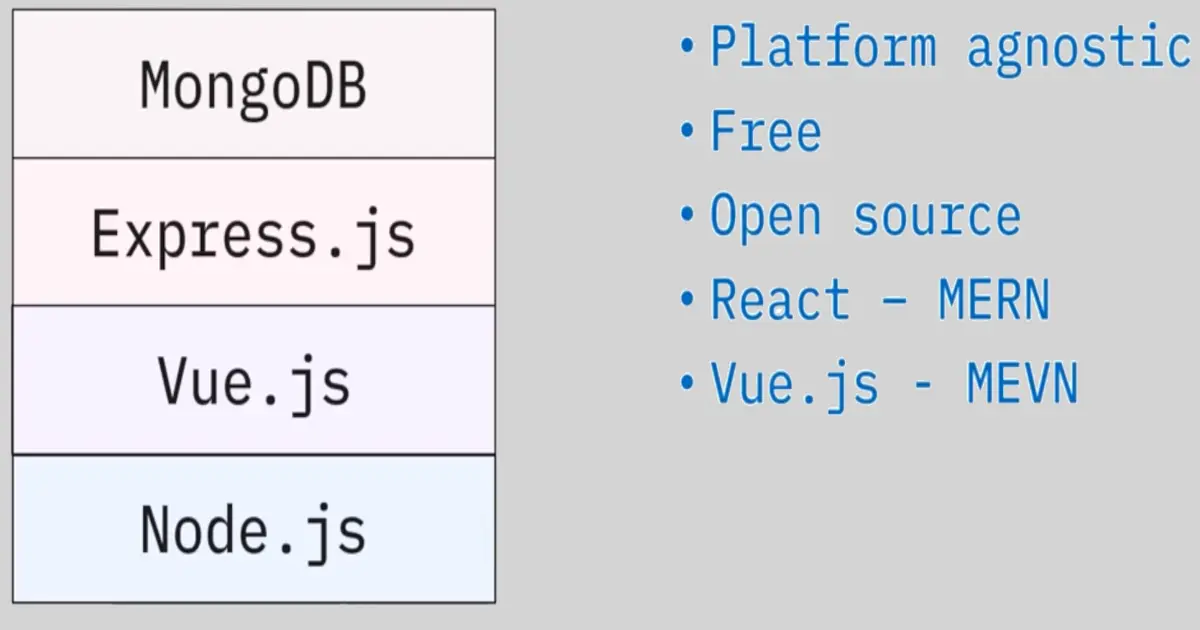
MEAN
-
MEVN
-
MERN
LAMP Stack:
MEAN and relasted stacks:
Comparison of MEAN, MEVN, and LAMP:
- MEAN
- All parts use JS – one language to learn
- Lost of documentation and reusable code
- Not suited to large-scale applications or relational data
- MEVN
- Similar to MEAN
- Less reusable libs
- LAMP
- Lots of reusable code and support
- Only on Linux
- Not suited in non-relational data
- Uses different languages