Data Loss Prevention and Mobile Endpoint Protection
What is Data Security and Protection?
Protecting the:
-
Confidentiality
-
Integrity
-
Availability
Of Data:
-
In transit
-
At rest
- Databases
- Unstructured Data (files)
- On endpoints
What are we protecting against?
Deliberate attack:
-
Hackers
-
Denial of Service
Inadvertent attacks:
-
Operator error
-
Natural disaster
-
Component failure
Data Security Top Challenges
- Explosive data growth
- New privacy regulations (GDPR, Brazil’s LGPD etc.)
- Operational complexity
- Cybersecurity skills shortage
Data Security Common Pitfalls
Five epic fails in Data Security:
- Failure to move beyond compliance
- Failure to recognize the need for centralized data security
- Failure to define who owns the responsibility for the data itself
- Failure to address known vulnerabilities
- Failure to prioritize and leverage data activity monitoring
Industry Specific Data Security Challenges
Healthcare
- Process and store combination of personal health information and payment card data.
- Subject to strict data privacy regulations such as HIPAA.
- May also be subject to financial standards and regulations.
- Highest cost per breach record.
- Data security critical for both business and regulatory compliance.
Transportation
- Critical part of national infrastructure
- Combines financially sensitive information and personal identification
- Relies on distributed IT infrastructure and third party vendors
Financial industries and insurance
- Most targeted industry: 19% of cyberattacks in 2018
- Strong financial motivation for both external and internal attacks
- Numerous industry-specific regulations require complex compliance measures
Retail
- Among the most highly targeted groups for data breaches
- Large number of access points in retail data lifecycle
- Customers and associates access and share sensitive data in physical outlets, online, mobile applications
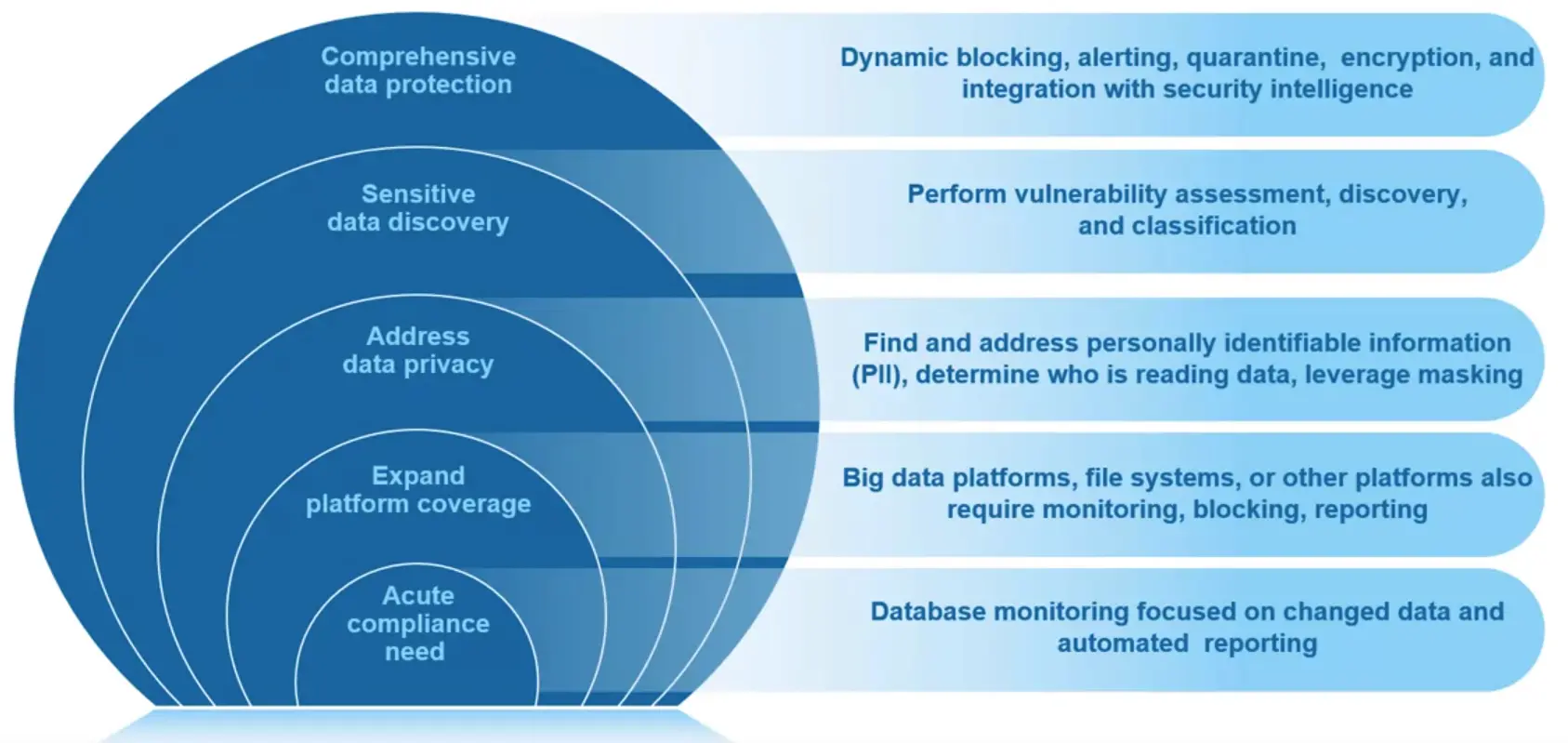
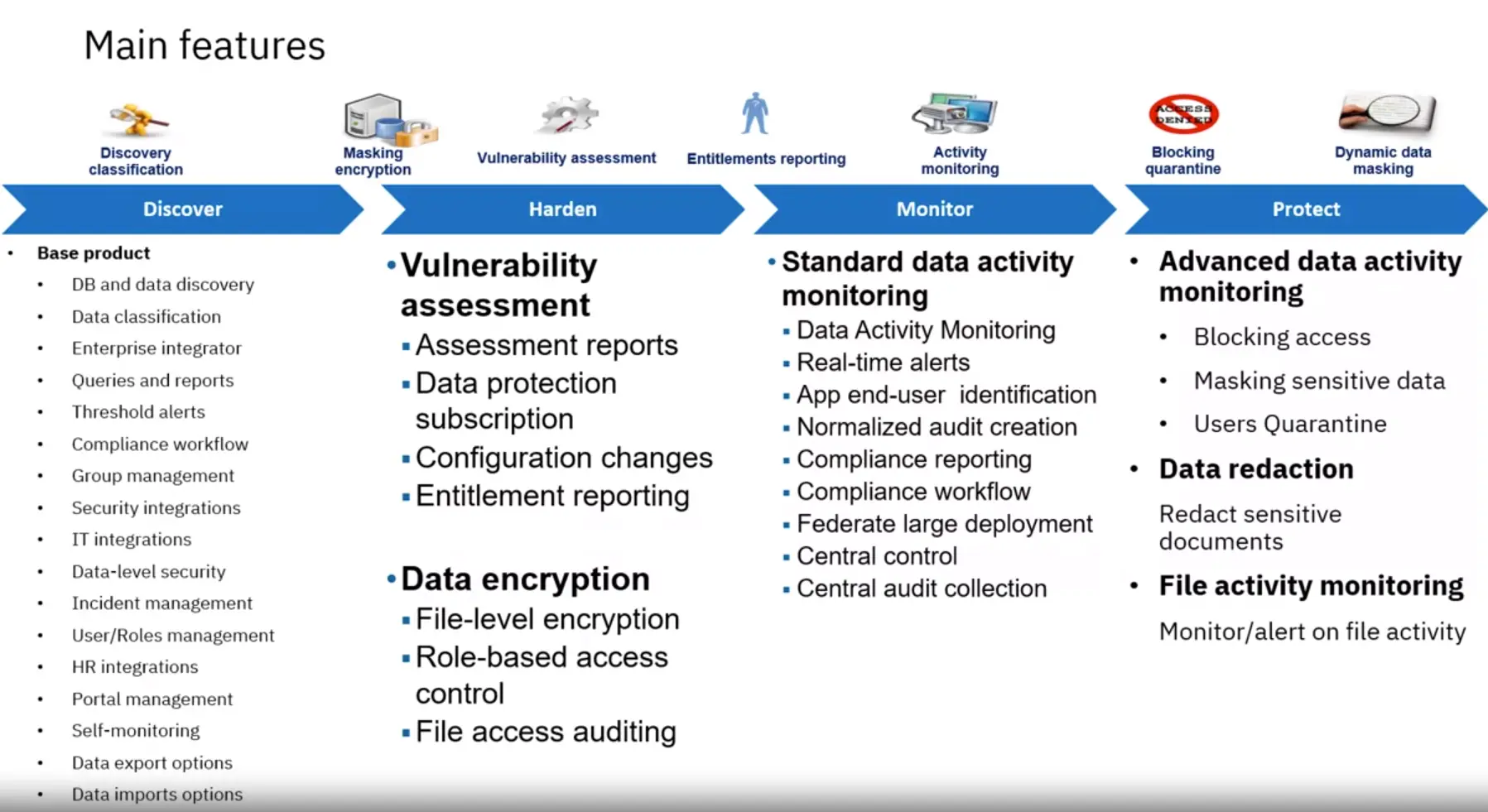
Capabilities of Data Protection
The Top 12 critical data protection capabilities:
- Data Discovery
- Where sensitive data resides
- Cross-silo, centralized efforts
- Data Classification
- Parse discovered data sources to determine the kind of data
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Determine areas of weakness
- Iterative process
- Data Risk analysis
- Identify data sources with the greatest risk exposure or audit failure and help prioritize where to focus first
- Build on classification and vulnerability assessment
- Data and file activity monitoring
- Capture and record real-time data access activity
- Centralized policies
- Resource intensive
- Real-time Alerting
- Blocking Masking, and Quarantining
- Obscure data and/or blocking further action by risky users when activities deviate from regular baseline or pre-defined policies
- Provide only level of access to data necessary
- Active Analytics
- Capture insight into key threats such as, SQL injections, malicious stored procedures, DoS, Data leakage, Account takeover, data tampering, schema tampering etc
- Develop recommendations for actions to reduce risk
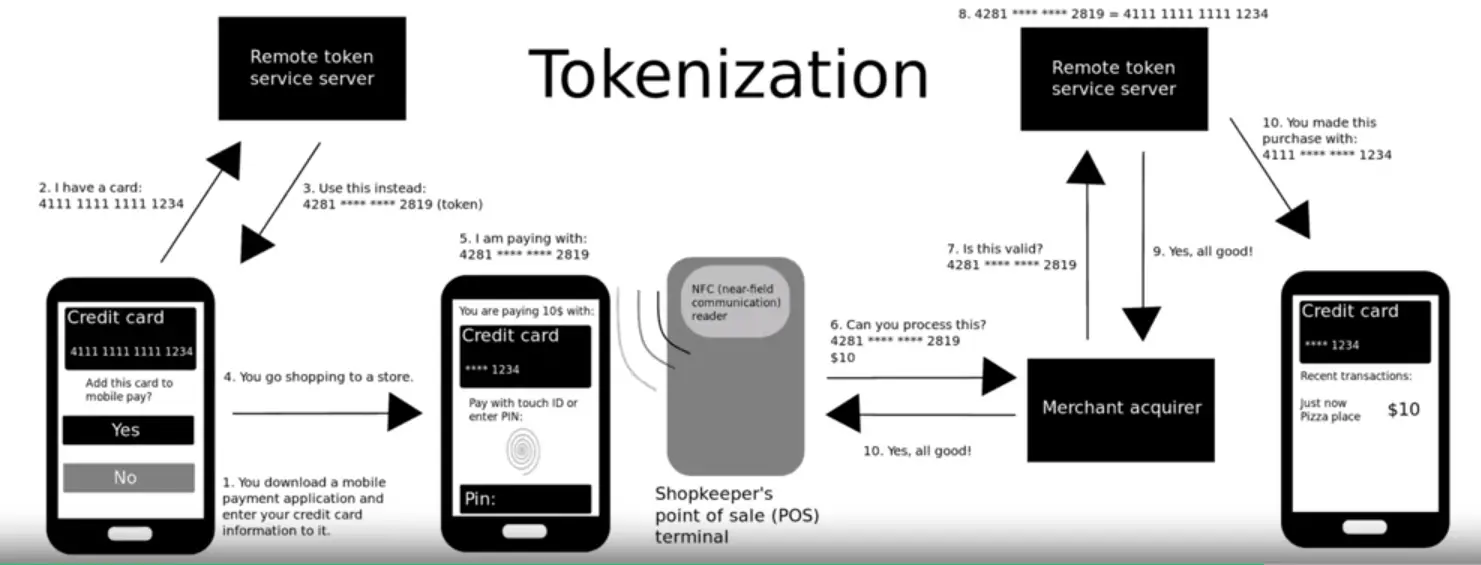
- Encryption
- Tokenization
- A special type of format-preserving encryption that substitutes sensitive data with a token, which can be mapped to the original value
- Key Management
- Securely distribute keys across complex encryption landscape
- Centralize key management
- Enable organized, secure key management that keeps data private and compliant
- Automated Compliance Report
- Pre-built capabilities mapped to specific regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, CCPA and so on
- Includes:
- Audit workflows to streamline approval processes
- Out-of-the-box reports
- Pre-built classification patterns for regulated data
- Tamper-proof audit repository
Data Protection – Industry Example
Guardium support the data protection journey
Guardium – Data Security and Privacy
- Protect all data against unauthorized access
- Enable organizations to comply with government regulations and industry standards
Mobile Endpoint Protection
iOS
-
Developed by Apple
-
Launched in 2007
-
~13% of devices (based on usage)
-
~60% of tablets worldwide run iOS/iPadOS
-
MDM capabilities available since iOS 6
Android
-
Android Inc. was a small team working on an alternative to Symbian and Windows Mobile OS.
-
Purchased by Google in 2005 – the Linux kernel became the base of the Android OS. Now developed primarily by Google and a consortium known as Open Handset Alliance.
-
First public release in 2008
-
~86% of smartphones and ~39% of tablets run some form of Android.
-
MDM capabilities since Android 2.2.
How do mobile endpoints differ from traditional endpoints?
- Users don’t interface directly with the OS.
- A series of applications act as a broker between the user and the OS.
- OS stability can be easily monitored, and any anomalies reported that present risk.
- Antivirus software can “see” the apps that are installed on a device, and reach certain signatures, but can not peek inside at their contents.
Primary Threats To Mobile Endpoints
System based:
-
Jailbreaking and Rooting exploit vulnerabilities to provide root access to the system.
-
Systems that were previously read-only can be altered in malicious ways.
-
One primary function is to gain access to apps that are not approved or booting.
-
Vulnerabilities and exploits in the core code can open devices to remote attacks that provide root access.
App based threats:
-
Phishing scams – via SMS or email
-
Malicious code
-
Apps may request access to hardware features irrelevant to their functionality
-
Web content in mobile browsers, especially those that prompt for app installations, can be the root cause of many attacks
External:
-
Network based attacks
-
Tethering devices to external media can be exploited for vulnerabilities
-
Social engineering to unauthorized access to the device
Protection mobile assets
- MDM: Control the content allowed on the devices, restrict access to potentially dangerous features.
- App security: Report on the health and reliability of applications, oftentimes before they even make it on the devices.
- User Training
Day-to-day operations
While it may seem like a lot to monitor hundreds, thousands, or hundreds of thousands of devices daily, much of the information can be digested by automated systems and action taken without much admin interactions.