Subsections of Cybersecurity Roles, Proces and OS Security
People Processes and Technology
Frameworks and their Purpose
Best practices, baseline, and frameworks
- Used to improve the controls, methodologies, and governance for the IT departments or the global behavior of the organization.
- Seeks to improve performance, controls, and metrics.
- Helps to translate the business needs into technical or operational needs.
Normative and Compliance
- Rules to follow for a specific industry.
- Enforcement for the government, industry, or clients.
- Event if the company or the organization do not want to implement those controls for compliance.
Best practices, frameworks & others
- Frameworks
-
COBIT (Control Objective for Information and Related Technologies)
COBIT is a framework created by ISACA for IT management and IT governance. The framework is business focused and defines a set of generic processes for the management of IT, with each process defined together.
-
ITIL (The Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
ITIL is a set of detailed practices for IT activities such as IT service management (ITSM) and IT asset management (ITAM) that focus on aligning IT services with the needs of business.
-
ISOs (International Organization for Standardization)
-
COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organization of the Tread way Commission)
COSO is a joint initiative to combat corporate fraud.
- Project manager methodologies
- Industry best practices
- Developer recommendations
- Others
Roles in Security
- CISO (Chief Information Security Officer)
The CISO is a high-level management position responsible for the entire computer security department and staff.
- Information Security Architect
- Information Security Consultant/Specialist
- Information Security Analyst
This position conducts Information security assessments for organizations and analyzes the events, alerts, alarms and any Information that could be useful to identify any threat that could compromise the organization.
- Information Security Auditor
This position is in charge of testing the effectiveness of computer information systems, including the security of the systems, and reports their findings.
- Security Software Developer
- Penetration Tester / Ethical Hacker
- Vulnerability Assessor
etc.
Business Process Management (BPM) and IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Basics
Introduction to Process
- Processes and tools should work in harmony
- Security Operations Centers (SOC) need to have the current key skills, tools, and processes to be able to detect, investigate and stop threats before they become costly data breaches.
- As volumes of security alerts and false positives grow, more burden is placed upon Security Analyst and Incident Response Teams.
Business Process Management (BPM) Overview
“A set of defined repeatable steps that take inputs, add value, and produce outputs that satisfy a customer’s requirements.”
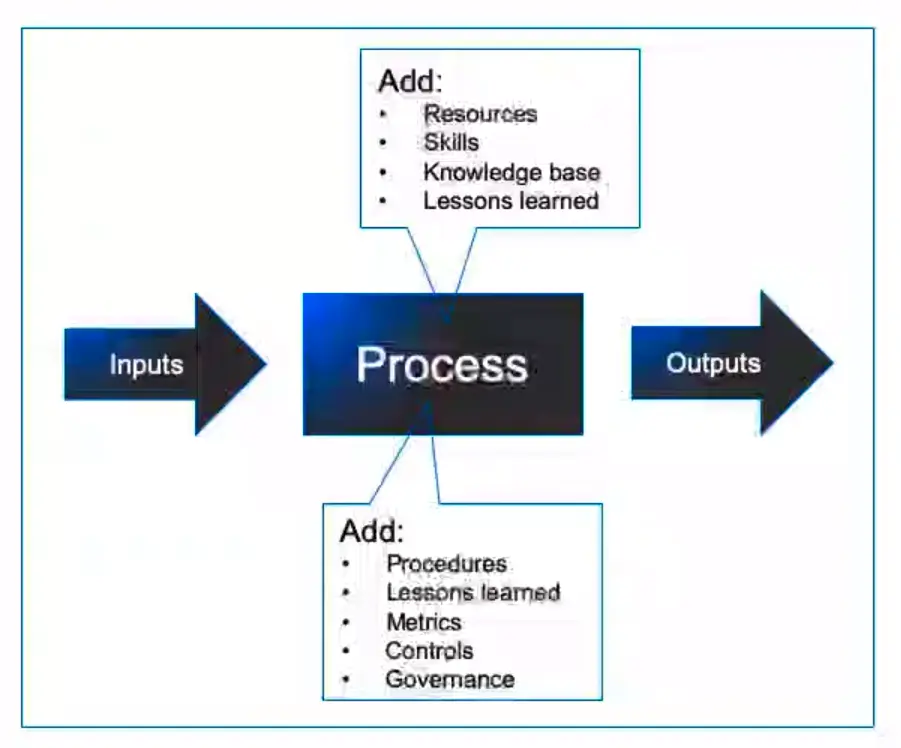

Attributes of a Process
- Inputs:
Information or materials that are required by the process to get started.
- Outputs:
Services, or products that satisfy customer requirements.
- Bounds/Scope:
The process starts when and end when.
- Tasks/Steps:
Actions that are repeatable.
- Documentation:
For audit, compliance, and reference purposes.
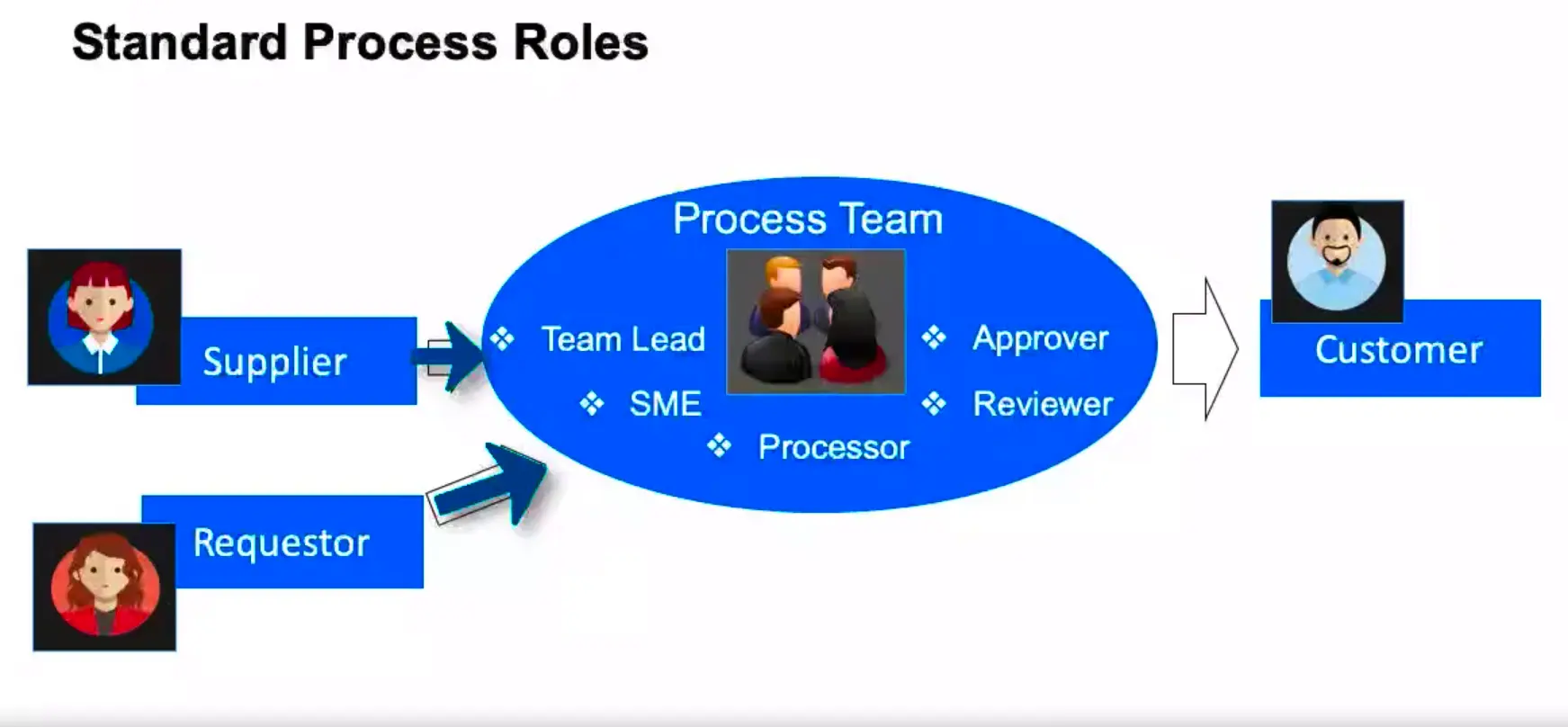
Standard Process Roles

What makes a Process Successful?
- Charter
- Clear Objectives
- Governance/Ownership
- Repeatability (reduced variation)
- Automation
- Established Performance indicators (metrics)
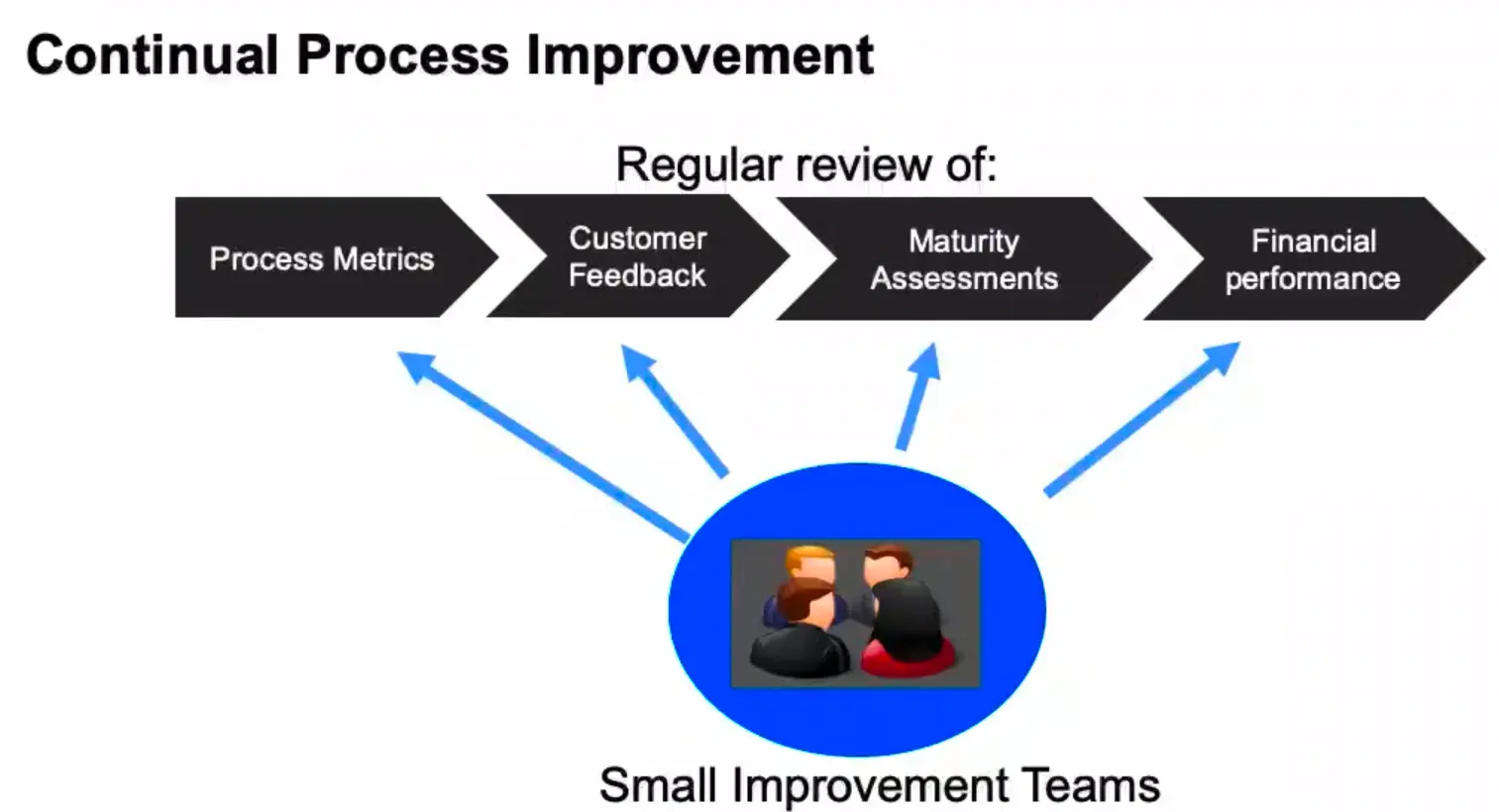
“It is critical that we measure our processing, so understand if they are performing to specifications and producing the desired outcome every time; and within financial expectations.”
- Typical Categories
- Cycle Time
- Cost
- Quality (Defect Rate)
- Rework
Continual Process Improvement

- ITIL is a best practice framework that has been drawn from both the public and private sectors internationally.
- It describes how IT resources should be organized to deliver Business value.
- It models how to document processes and functions, in the roles of IT Service Management (ITSM).
- ITIL Life-cycle – Service Phases
- Service Strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operations
- Service Improvements
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Strategy
- Service Portfolio Management
- Financial Management
- Demand Management
- Business Relationship Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Design
- Service Catalog Management
- Service Level Management
- Information Security Management
- Supplier Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Transition
- Change Management
- Project Management
- Release & Deployment Management
- Service validation & Testing
- Knowledge Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Service Operations
- Event Management
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
ITIL Life-cycle – Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
- Review Metrics
- Identify Opportunities
- Test & Prioritize
- Implement Improvements
Key ITIL Processes
Problem Management
- The process responsible for managing the Life-cycle of all problems.
ITIL defines a ‘problem’ as ‘an unknown cause of one or more incidents.’
Change Management
- Manage changes to baseline service assets and configuration items across the ITIL Life-cycle.
Incident Management
-
An incident is an unplanned interruption to an IT Service, a reduction in the quality of an IT Service, and/ or a failure of a configuration item.
Log → Assign → Track → Categorize → Prioritize → Resolve → Close
Event Management
- Events are any detectable or discernible occurrence that has significance for the management of IT Infrastructure, or the delivery of an IT service.
Service Level Management
- This involves the planning coordinating, drafting, monitoring, and reporting on Service Level Agreements (SLAs). It is the ongoing review of service achievements to ensure that the required service quality is maintained and gradually improved.
- This deals with having and maintaining an information security policy (ISP) and specific security Policies that address each aspect of strategy, Objectives, and regulations.
Difference between ITSM and ITIL
“ITSM is a concept that enables an organization to maximize business value from the use of information Technology.”
IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL)
“ITIL is a best practice framework that gives guidance on how ITSM can be delivered.”
Further discussion of confidentiality, integrity, and availability
Who are Alice, Bob, and Trudy?
-
Well known in network security world.
-
Bob, Alice (friends) want to communicate “securely”.
-
Trudy (intruder) may intercept, delete, add messages.
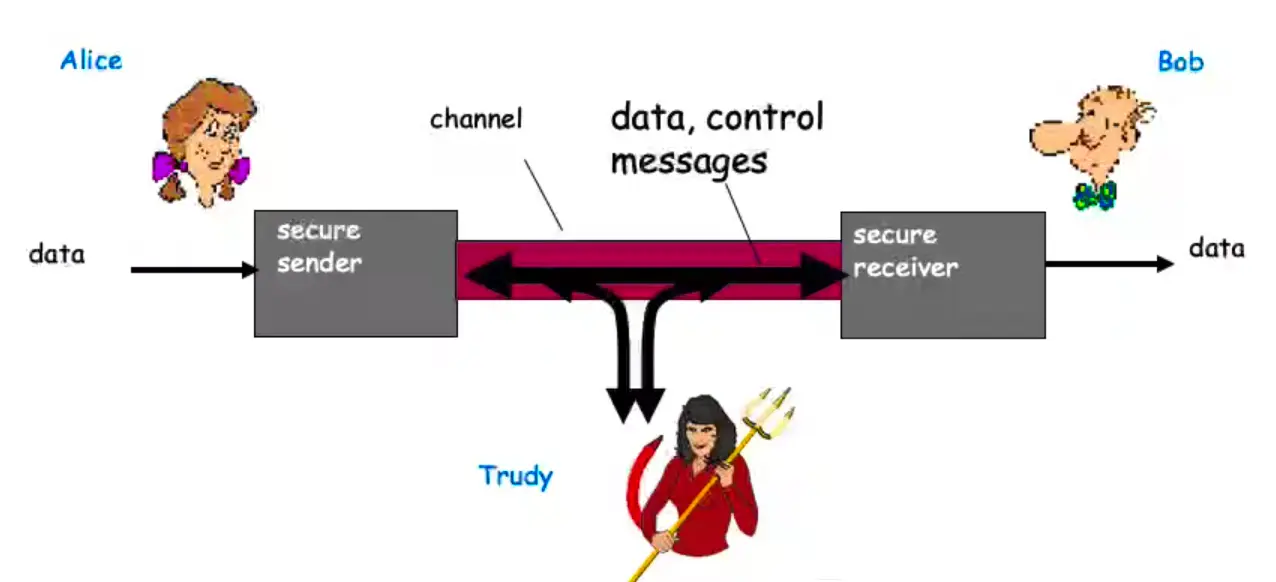

Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
- Main components of network security.
Confidentiality
- Preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary information.
- Loss of confidentiality is the unauthorized disclosure of information.
Integrity
- Guarding against improper information modification or destruction.
- Including ensuring information non-repudiation and authenticity.
- Integrity loss is the unauthorized modification or destruction of information.
Availability
- Timely and reliable access to information.
- Loss of availability is the disruption of access to an information system.
Authenticity and Accountability
- Authenticity: property of being genuine and verifiable.
- Accountability: mapping actions to an identity.
Identification and AAA
- Security token
- Password
- Biometrics
Identification → Authentication → Authorization → Accountability
Authentication methods
- Something you know
- Something you have
- Something you are
- Fingerprints
- Retina Scanners
- Biometric Signals
Control Types
- Administrative
- Technical
- Physical
Each control type can be
- Corrective
- Preventive
- Dissuasive
- Recovery
- Detective
- Compensatory
Access Control Methods
“Only who has the rights to access or utilize the resources can use them.”
Access control models
MAC – Mandatory Access Control
-
Use labels to regulate the access
-
Military use
DAC – Discretionary Access Control
-
Each object (folder or file) has an owner and the owner defines the rights and privilege
Role Based Access Control
The rights are configured based on the user roles. For instance, sales group, management group, etc.
Other methods
Centralized
Best practices for the access control field
These concepts are deeply integrated with the access control methodologies and must be followed by the organization in order of the policies and procedures.
- Least privilege
- Separation of duties
- Rotation of duties
Access Control – Physical and Logical
Physical access control methods
Logical access control methods
- ACL (Routers)
- GPO’S
- Password policies
- Device policies
- Day and time restrictions
- Accounts
- Centralized
- Decentralized
- Expiration
BYOD, BYOC … BYO Everything…
Popular concepts for moderns times. Each collaborator has the opportunity to bring their own device to the work environment.
Some controls to follow:
- Strict policy and understanding
- Use of technical control MDM
- Training
- Strong perimetral controls
Monitoring the access control process
- IDS/IPs
- HOST IDS and IPS
- Honeypot
- Sniffers
Operating System Security Basics
User and Kernel Modes
MS Windows Components
- User Mode and Kernel Mode
- Drivers call routines that are exported by various kernel components.
- Drivers must respond to specific calls from the OS and can respond to other system calls.
User Mode
- When you start a user-mode application, Windows creates a process for the application.
- Private virtual address space
- Private handle table
- Each application runs in isolation and if an application crashes, the crash is limited to that one application.
Kernel Mode
- All code that runs in kernel mode shares a single virtual address space.
- If a kernel-mode driver accidentally writes to the wrong virtual address, data that belongs to the OS or another driver could be compromised.
- If a kernel-mode driver crashes, the entire OS crashes.
File System
Types of File Systems
NTS (New Technology File System)
-
Introduced in 1993
-
Most common file system for Windows end user systems
-
Most Windows servers use NTFS as well
FATxx (File Allocation Table)
-
Simple File system used since the 80s
-
Numbers preceding FAT refer to the number of bits used to enumerate a file system block. Ex FAT16, FAT32
-
Now mainly used for removable devices under 32 GB capacity.
(NOTE: FAT32 actually support upto ≤2TB storage size).
Directory Structure
Typical Windows Directory Structure
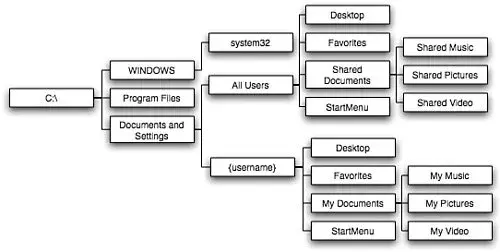

Shortcuts and Commands
Windows Shortcuts
Additional Shortcuts
- F2: Rename
- F5: Refresh
- Win+L: Lock your computer
- Win+I: Open Settings
- Win+S: Search Windows
- Win+PrtScn: Save a screenshot
- Ctrl+Shift+Esc: Open the Task Manager
- Win+C: Start talking to Cortana
- Win+Ctrl+D: Add a new virtual desktop
- Win+X: Open the hidden Menu
Linux Key Components
Key Components
Linux has two major components:
- The Kernel
- It is the core of the OS. It interacts directly with the hardware.
- It manages system and user input/output. Processes, files, memory, and devices.
1) The Shell
- It is used to interact with the kernel.
- Users input commands through the shell and the kernel performs the commands.
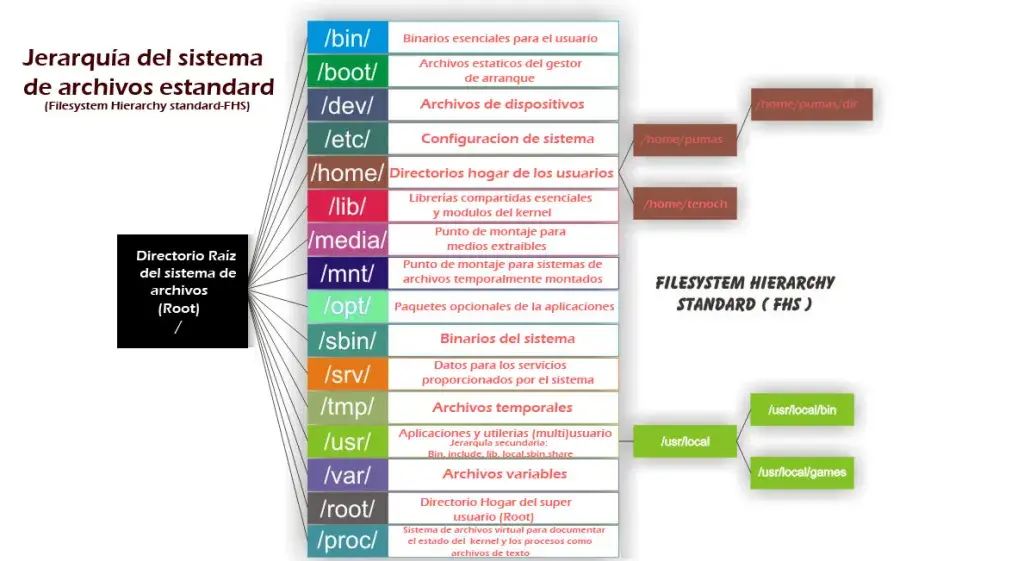
Linux File Systems
File Systems
- represents file in CLId represents directory in CLI

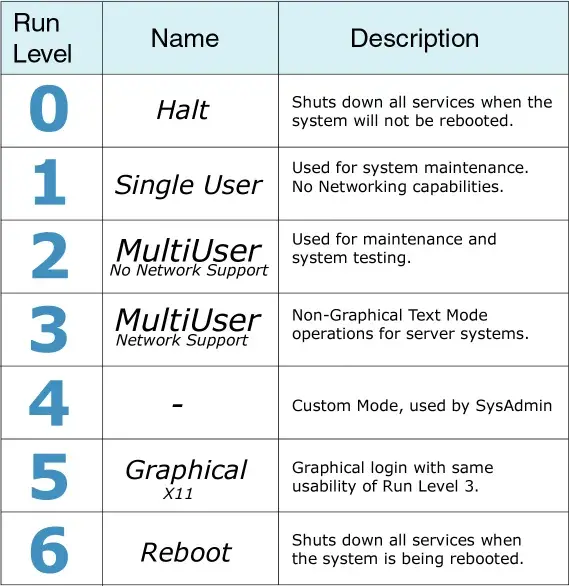
Run Levels

Linux Basic Commands
cd: change directorycp: copy files or dirsmv: move file or dirsls: lists info related to files and dirsdf: display file system disk spacekill: stop an executing processrm: delete file and dirsrmdir: remove en empty dircat: to see the file contents, or concatenate multiple files togethermkdir: creates new dirifconfig: view or configure network interfaceslocate: quickly searches for the location of files. It uses an internal database that is updated using updatedb command.tail: View the end of a text file, by default the last 10 linesless: Very efficient while viewing huge log files as it doesn’t need to load the full file while openingmore: Displays text, one screen at a timenano: a basic text editorchmod: changes privileges for a file or dir
Permissions and Owners
File and directory permission
- There are three groups that can ‘own’ a file.
- For each group there are also three types of permissions: Read, Write, and Execute.
- Read: 4(100), Write: 2(010), Execute: 1(001)
Change Permissions
You can use the chmod command to change the permissions of a file or dir:
chmod <permissions><filename>chmod 755<filename>chmod u=rw,g=r,o=r<filename>
Change owner
You can change the owner and group owner of a file with the chown command:
chown <user>:<group><filename>
macOS Security Overview
macOS Auditing
About My mac menu, contains information about
- OS
- Displays
- Storage
- Support
- Service
- Logs, etc.
Activity Monitor real-time view of system resource usage and relevant actionsConsole, contains
- Crash reports
- Spin reports
- Log reports
- Diagnostic reports
- Mac Analysis Data
- System.log
macOS Security Settings
Various Security settings for macOS can be found in System Preferences app.
Genral Tab offers GateKeeper settings for installing apps from other AppStore, and few other settings.FileVault Tab contains information about system and file encryption.FireWall Tab for system level software firewall settings with basic and to advanced options.Privacy Tab contains location services and other privacy related info and settings.
macOS Recovery
- macOS comes with a hidden partition installed called macOS Recovery, it essentially replaces the installation discs that comes with new computers.
- Access it by restarting your Mac while holding the
R key.
- It offers following tools/options:
Restore from the Time Machine BackupReinstall macOSGet Help OnlineDisk Utility
Virtualization Basics and Cloud Computing
An Overview of Virtualization
- Allows you to create multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from a single, physical hardware system.
- Hypervisor/Host
- Virtual Machine/Guest
Hypervisor
- Separate the physical resources from the virtual environments
- Hypervisors can sit on top of an OS (end user) or be installed directly onto hardware (enterprise).
Virtual Machine
- The virtual machine functions as a single data file.
- The hypervisor relays requests from the VM to the actual hardware, is necessary.
- VMs doesn’t interact directly with the host machine.
- Physical hardware is assigned to VMs.
Virtualization to Cloud
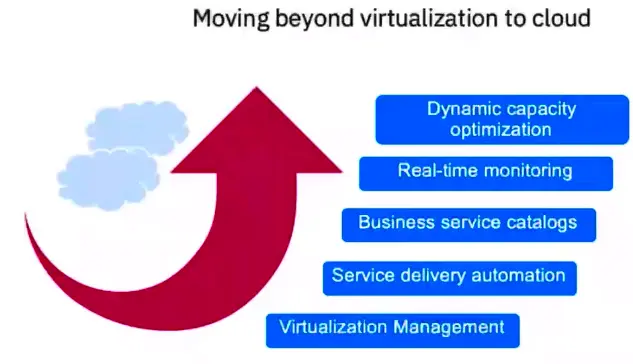

Cloud Deployments
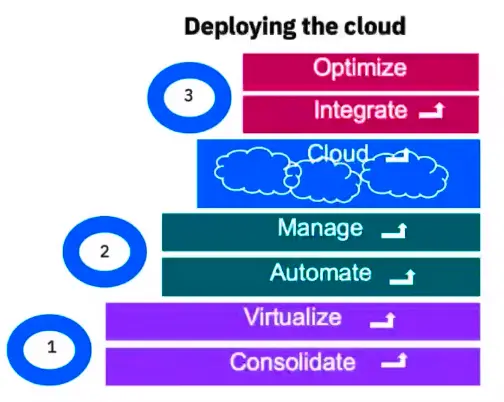

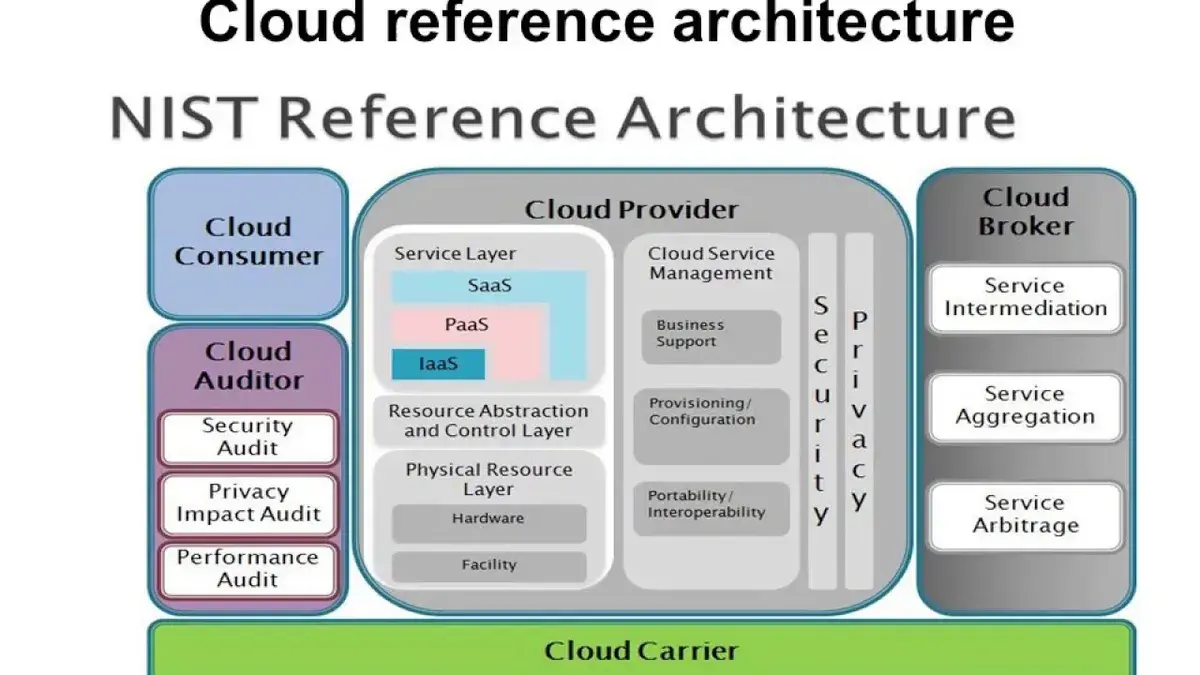
Cloud Computing Reference Model