Operating System Security Basics
User and Kernel Modes
MS Windows Components
- User Mode and Kernel Mode
- Drivers call routines that are exported by various kernel components.
- Drivers must respond to specific calls from the OS and can respond to other system calls.
User Mode
- When you start a user-mode application, Windows creates a process for the application.
- Private virtual address space
- Private handle table
- Each application runs in isolation and if an application crashes, the crash is limited to that one application.
Kernel Mode
- All code that runs in kernel mode shares a single virtual address space.
- If a kernel-mode driver accidentally writes to the wrong virtual address, data that belongs to the OS or another driver could be compromised.
- If a kernel-mode driver crashes, the entire OS crashes.
File System
Types of File Systems
NTS (New Technology File System)
-
Introduced in 1993
-
Most common file system for Windows end user systems
-
Most Windows servers use NTFS as well
FATxx (File Allocation Table)
-
Simple File system used since the 80s
-
Numbers preceding FAT refer to the number of bits used to enumerate a file system block. Ex FAT16, FAT32
-
Now mainly used for removable devices under 32 GB capacity.(NOTE: FAT32 actually support upto ≤2TB storage size).
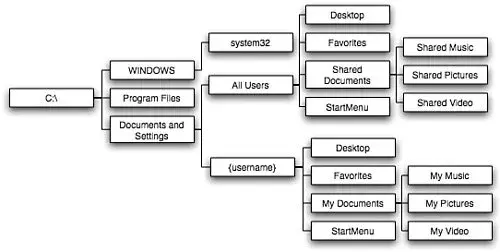
Directory Structure
Typical Windows Directory Structure
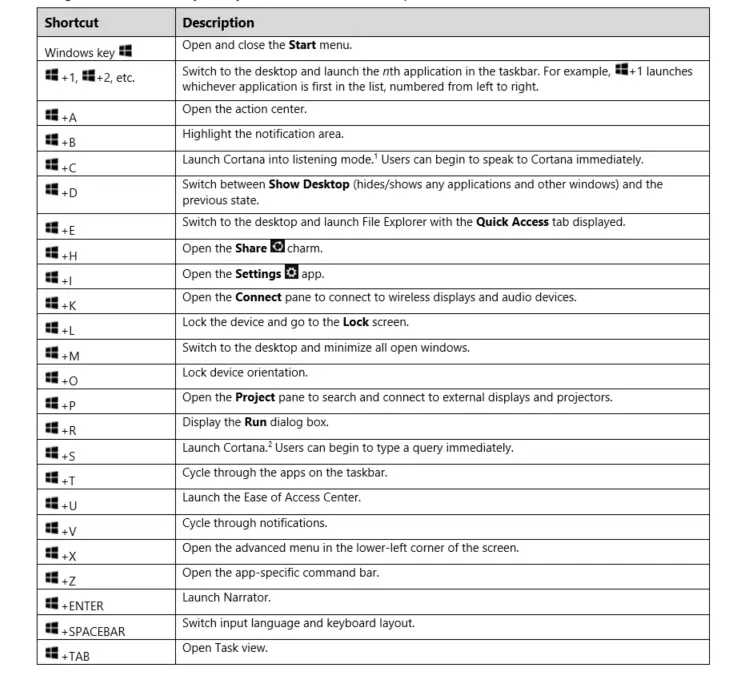
Shortcuts and Commands
Windows Shortcuts
-
Common tasks that can be accessed using the Windows or Ctrl Key and another Key.
-
Time saving and helpful for tasks done regularly.
Additional Shortcuts
- F2: Rename
- F5: Refresh
- Win+L: Lock your computer
- Win+I: Open Settings
- Win+S: Search Windows
- Win+PrtScn: Save a screenshot
- Ctrl+Shift+Esc: Open the Task Manager
- Win+C: Start talking to Cortana
- Win+Ctrl+D: Add a new virtual desktop
- Win+X: Open the hidden Menu
Linux Key Components
Key Components
Linux has two major components:
- The Kernel - It is the core of the OS. It interacts directly with the hardware. - It manages system and user input/output. Processes, files, memory, and devices. 1) The Shell - It is used to interact with the kernel. - Users input commands through the shell and the kernel performs the commands.
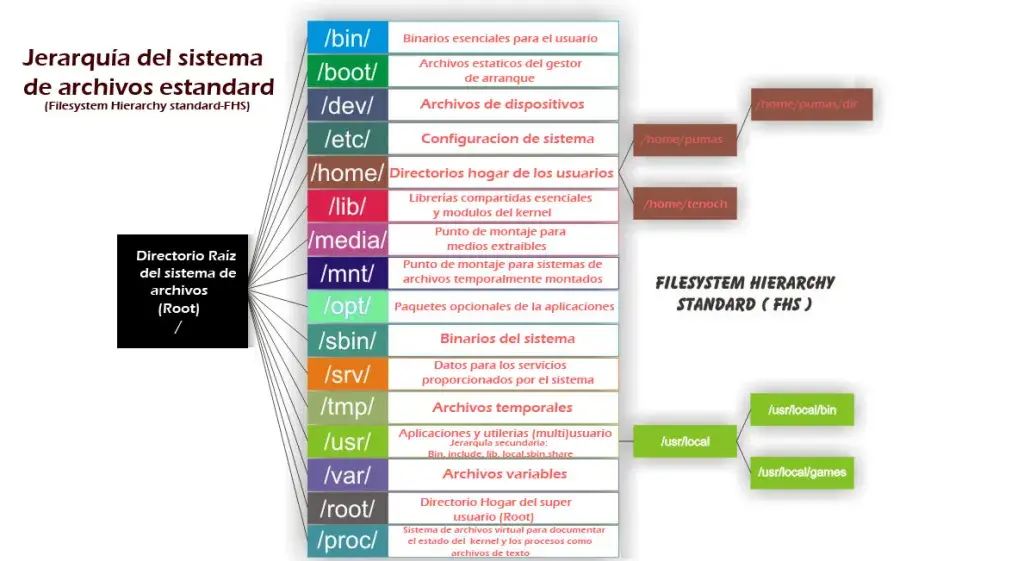
Linux File Systems
File Systems
-represents file in CLIdrepresents directory in CLI
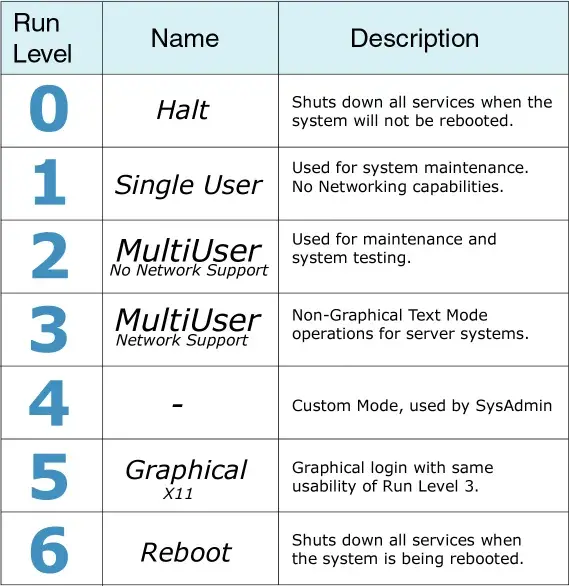
Run Levels
Linux Basic Commands
cd: change directorycp: copy files or dirsmv: move file or dirsls: lists info related to files and dirsdf: display file system disk spacekill: stop an executing processrm: delete file and dirsrmdir: remove en empty dircat: to see the file contents, or concatenate multiple files togethermkdir: creates new dirifconfig: view or configure network interfaceslocate: quickly searches for the location of files. It uses an internal database that is updated usingupdatedbcommand.tail: View the end of a text file, by default the last 10 linesless: Very efficient while viewing huge log files as it doesn’t need to load the full file while openingmore: Displays text, one screen at a timenano: a basic text editorchmod: changes privileges for a file or dir
Permissions and Owners
File and directory permission
- There are three groups that can ‘own’ a file.
- User
- group
- everybody
- For each group there are also three types of permissions: Read, Write, and Execute.
- Read: 4(100), Write: 2(010), Execute: 1(001)
Change Permissions
You can use the chmod command to change the permissions of a file or dir:
chmod <permissions><filename>chmod 755<filename>chmod u=rw,g=r,o=r<filename>
Change owner
You can change the owner and group owner of a file with the chown command:
chown <user>:<group><filename>
macOS Security Overview
macOS Auditing
About My macmenu, contains information about- OS
- Displays
- Storage
- Support
- Service
- Logs, etc.
Activity Monitorreal-time view of system resource usage and relevant actionsConsole, contains- Crash reports
- Spin reports
- Log reports
- Diagnostic reports
- Mac Analysis Data
- System.log
macOS Security Settings
Various Security settings for macOS can be found in System Preferences app.
GenralTab offersGateKeepersettings for installing apps from other AppStore, and few other settings.FileVaultTab contains information about system and file encryption.FireWallTab for system level software firewall settings with basic and to advanced options.PrivacyTab contains location services and other privacy related info and settings.
macOS Recovery
- macOS comes with a hidden partition installed called macOS Recovery, it essentially replaces the installation discs that comes with new computers.
- Access it by restarting your Mac while holding the
Rkey.
- Access it by restarting your Mac while holding the
- It offers following tools/options:
Restore from the Time Machine BackupReinstall macOSGet Help OnlineDisk Utility