Defense in Depth
System Hardening
Intro to Defense in Depth
The concept of having multiple, overlapping systems of defense to protect IT systems.
Disabling Unnecessary Components
Two important security risk mitigation components:
- Attack Vectors
- Attack surfaces
The less complex something is, the less likely there will be undetected flaws.
Another way to keep things simple is to reduce your software deployments.
- Telnet access for a managed switch has no business being enabled in a real-world environment.
Attack vector
The method or mechanism by which an attacker or malware gains access to a network or system.
Attack surface
The sum of all the different attack vectors in a given system.
Host-Based Firewall
Protect individuals hosts from being compromised when they’re used in untrusted, potentially malicious environments.
A host-based firewall plays a big part in reducing what’s accessible to an outside attacker.
If the users of the systems have administrator rights, then they have the ability to change firewall rules and configuration.
Bastion Hosts
Bastion hosts are specially hardened and minimized in terms of what is permitted to run on them. Typically, bastion hosts are expected to be exposed to the internet, so special attention is paid to hardening and locking them down to minimize the chances of compromise.
- These are servers that are specifically hardened and minimized to reduce what’s permitted to run on them.
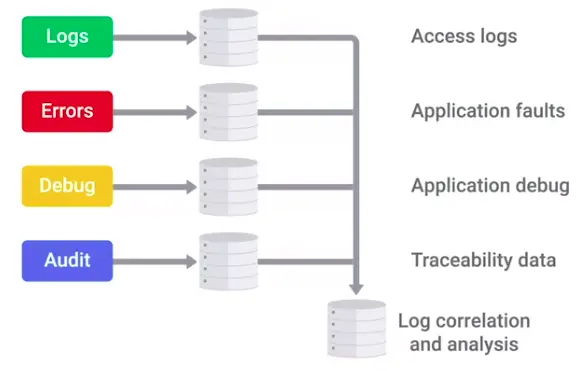
Logging and Auditing
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system is a centralized log management system.
Once logs are centralized and standardized, you can write an automated alerting based on rules.
Some open source logging servers SIEM solutions:
- rsyslog
- Splunk Enterprise Security
- IBM Security Qradar
- RSA Security Analytics
Antimalware Protection
Lots of unprotected systems would be compromised in a matter of minutes if directly connected to the internet without any safeguards or protections in place.
- Antivirus software will monitor and analyze things, like new files being created or being modified on the system, in order to watch for any behavior that matches a known malware signature.
- Antivirus software is just one piece of our anti-malware defenses.
- There are binary whitelisting defense software, that only allow white listed programs on the system.
Is antivirus really that useful? Sophos antivirus was maliciously compromised. How hackers bypassed the binary whitelisting defenses?
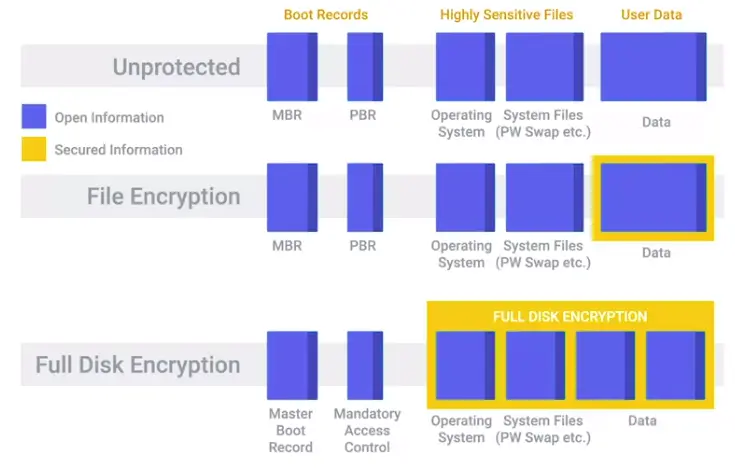
Disk Encryption
Home directory or file-based encryption only guarantees confidentiality and integrity of files protected by encryption.
Full-disk encryption (FDE)
Works by automatically converting data on a hard drive into a form that cannot be understood by anyone who doesn’t have the key to “undo” the conversation.
- When you implement a full disk encryption solution at scale, it’s super important to think how to handle cases where passwords are forgotten.
Key Escrow
Allows the encryption key to be securely stored for later retrieval by an authorized party.
Application Hardening
Software Patch Management
As an IT Support Specialist, it’s critical that you make sure that you install software updates and security patches in a timely way, in order to defend your company’s systems and networks.
The best protection is to have a good system and policy in place for your company.
Critical infrastructure devices should be approached carefully when you apply updates. There’s always the risk that a software update will introduce a new bug that might affect the functionality of the device.
Browser Hardening
The methods include evaluating sources for trustworthiness, SSL certificates, password managers, and browser security best practices. Techniques for browser hardening are significant components in enterprise-level IT security policies. These techniques can also be used to improve internet security for organizations of any size and for individual users.
Identifying trusted versus untrusted sources
- Use antivirus and anti-malware software and browser extensions
- Check for SSL certificates
- Ensure the URL displayed in the address bar shows the correct domain name.
- Search for negative reviews of the website from trusted sources.
- Don’t automatically trust website links provided by people or organizations you trust.
- Use hashing algorithms for downloaded files.
Secure connections and sites
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates are issued by trusted certificate authorities (CA), such as DigiCert. An SSL certificate indicates that any data submitted through a website will be encrypted. A website with a valid SSL certificate has been inspected and verified by the CA. You can find SSL certificates by performing the following steps:
- Check the URL in the address bar. The URL should begin with the https:// protocol. If you see http:// without the “s”, then the website is not secure.
- Click on the closed padlock icon in the address bar to the left of the URL. An open lock indicates that the website is not secure.
- A pop-up menu should open. Websites with SSL certificates will have a menu option labeled “Connection is secure.” Click on this menu item.
- A new pop-up menu will appear with a link to check the certificate information. The layout and wording of this pop-up will vary depending on which browser you are using. When you review the certificate, look for the following items:
- The name of this suer – Make sure it is a trusted certificate authority.
- The domain it was issue to – This is name should match the website domain name.
- The expiration date – The certificate should not have passed its expiration date.
Note that cybercriminals can obtain SSL certificates too. So, this is not a guarantee that the site is safe. CAs also vary in how thorough they are in their inspections.
Application Policies
A common recommendation, or even a requirement, is to only support or require the latest version of a piece of software.
It’s generally a good idea to disallow risky classes of software by policy. Things like file sharing software and piracy-related software tend to be closely associated with malware infections.
Understanding what your users need to do their jobs will help shape your approach to software policies and guidelines.
Helping your users accomplish tasks by recommending or supporting specific software makes for a more secure environment.
Extensions that require full access to websites visited can be risky, since the extension developer has the power to modify pages visited.