Data Recovery and Backups
Planning for Data Recovery
What is Data Recovery?
“The process of trying to restore data after an unexpected even that results in data loss or corruption.”
How you go for data recovery depends on few factors:
- Nature of Data Loss
- Backups already in place
When an unexpected even occurs, your main objective is to resume normal operations asap, while minimizing the disruption to business functions.
The best way to be prepared for a data-loss event is to have a well-thought-out disaster plan and procedure in place.
- Disaster plans should involve making regular backups of any and all critical data that’s necessary for your ongoing business processes.
Postmortem
A Postmortem is a way for you to document any problems you discovered along the way, and most importantly, the ways you fixed them so, you can make sure they don’t happen again.
Backing Up Your Data
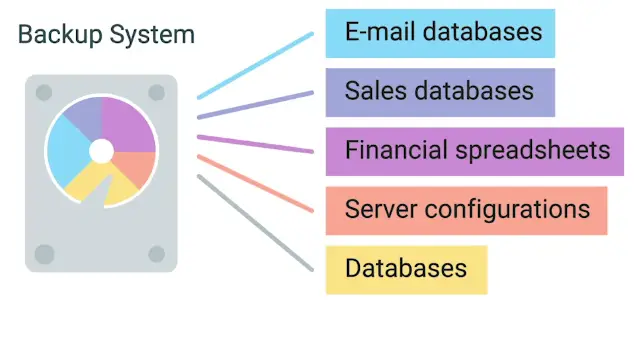
Absolutely necessary data should be backed up.
Backed up data as well as, data in transit for backup, both should be encrypted.
Backup Solutions
Too many backup solutions are there, some of them are:
rsync
A file transfer utility that’s designed to efficiently transfer and synchronize files between locations or computers.
Time Machine
Apple’s backup solution, that can restore entire snapshot or individual files.
Microsoft Backup and Restore
Backup and restore is used to back up files as well as, system snapshots in the disk.
This tool can do following tasks:
- Back up
- Create a system image
- Create a restore point
Testing Backups
Disaster recovery testing should be done every year or so.
Restoration procedure
Should be documented and accessible so that anyone with the right access can restore operations when needed.
Types of Backup
Ways to Perform Regular Backups:
- Full backup
- Differential backup
- Regular incremental backups
It’s a good practice to perform infrequent full backups, while also doing more frequent differential backups.
- While a differential backup backs up files that have been change or created since the last full backup, an incremental backup is when only the data that’s changed in files since the last incremental backup is backed up**.
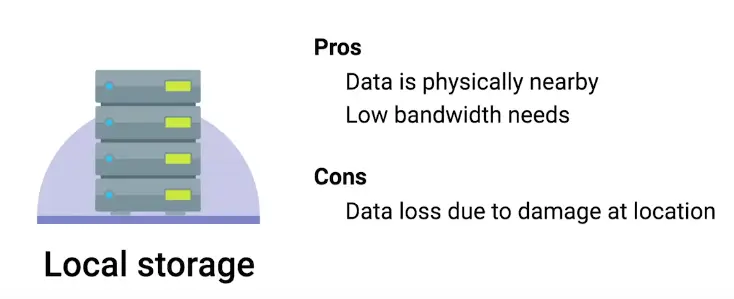
- RAID array can solve the problem of failing disks on on-site backups.
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)
A method of taking multiple physical disks and combining them into one large virtual disk.
- RAID isn’t a replacement for backups
- It’s data storage solution which can save you from accidental deletion, or malware.
User Backups
For user backups:
- Dropbox
- Apple iCloud
- Google Drive
Disaster Recovery Plans
What’s Disaster Recovery Plan?
“A collection of documented procedures and plans on how to react and handle an emergency or disaster scenario, from the operational perspective.”
Preventive measures
Any procedures or systems in place that will proactively minimize the impact of a disaster.
Detection measures
Meant to alert you and your team that a disaster has occurred that can impact operations.
- Environmental Sensors
- Flood sensors
- Temp and Humidity Sensors
- Evacuation procedures
Corrective or recovery measures
Those enacted after a disaster has occurred.
Designing Disaster Recovery Plan
No fit for all plan, there is a lot to go into a disaster recovery plan.
Designing a Disaster Recovery Plan:
- Perform Risk Assessment
- Determine Backup and Recovery Systems
- Determine Detection & Alert Measures & Test Systems
- Determine recovery measures
Risk assessment
Allows you to prioritize certain aspects of the organizations that are more at risk if there’s an unforeseen event.
Postmortems
What’s a Postmortem?
“A Postmortem is a way for you to document any problems you discovered along the way, and most importantly, the ways you fixed them so, you can make sure they don’t happen again.”
- We create a Postmortem after an incident, an outage, or some event when something goes wrong, or at the end of a project to analyze how it went.
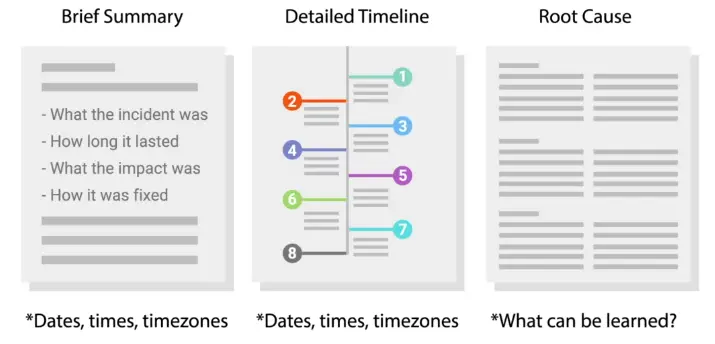
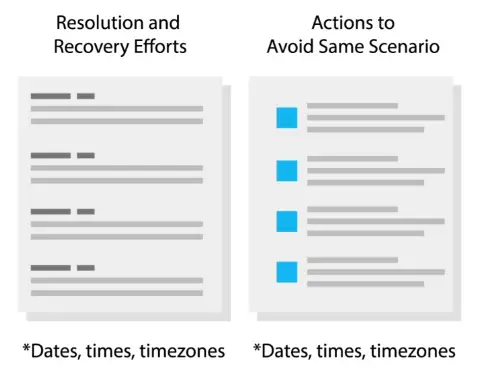
Writing a Postmortem
Typical postmortem report consists of: