The Network Layer
IP Addresses
-
32 bit long
-
4 octets describe in decimal number
-
Each octet range from 0 to 255
-
IP Addresses belong to Networks, not to the devices attached to those networks
When connecting to a network, an IP address is assigned automatically by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
IP address assigned by DHCP is called Dynamic IP address
-
Other type is static IP addresses
-
In most cases, static IP addresses are reserved for servers and networks devices, while Dynamic IP addresses are reserved for clients
IP Datagrams and Encapsulation
- IP Datagram
A highly structured series of fields that are strictly defined.
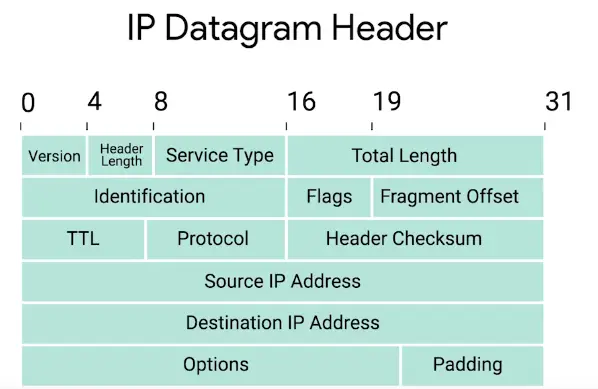
IP Datagram Header
-
Version
IPv4 is more common than IPv6
-
Header Length field
Almost always 20 bytes in length when dealing with IPv4
-
Service Type field
These 8 bits can be used to specify details about quality of service, or QoS, technologies
-
Total Length field
Indicates the total length of the IP datagram it’s attached to
-
Identification field
A 16-bit number that’s used to group messages together
The maximum size of a single datagram is the largest number you can represent with 16 bits which is 65535 If the total amount of data that needs to be sent is larger than what can fit in a single datagram, the IP layer needs to split this data up into many individual packets
-
Next are closely related Flags and Fragment Offset fields
-
Flags field
Used to indicate if a datagram is allowed to be fragmented, or to indicate that the datagram has already been fragmented
- Fragmentation
The process of taking a single IP datagram and splitting it up into several smaller datagrams
-
Time to Live (TTL) field
An 8-bit field that indicates how many router hops a datagram can transverse before it’s thrown away
-
Protocol field
Another 8-bit field that contains data about what transport layer protocol is being used, the most common ones are TCP and UDP
-
Header checksum field
A checksum of the contents of the entire IP datagram header
-
Source IP address (32-bits)
-
Destination IP address (32-bits)
-
IP Options field
An optional field and is used to set special characteristics for datagrams primarily used for testing purposes
-
Padding field
A series of zeros used to ensure the header is of correct total size, due to variable size to option field
Encapsulation
IP datagram is basically the payload section of network layer, the process involved is called Encapsulation.
- Entire content IP datagram are encapsulated in the form of IP payload of 3rd layer
IP Address Classes
Address class system
A way defining how the global IP address space is split up.
- Three Types of IP addresses, ClassA, ClassB, ClassC
- ClassA
Only first octet is used for network ID, rest is used for host ID.
- ClassB
Only the first two octets are used for network ID, the rest are used for host ID.
- ClassC
First three octets used for network ID, the last one used for host ID.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
A protocol used to discover the hardware address of a node with a certain IP address.
ARP table
A list of IP addresses and the MAC addresses associated with them.
- ARP table entries generally expire after a short amount of time to ensure changes in the network are accounted for.
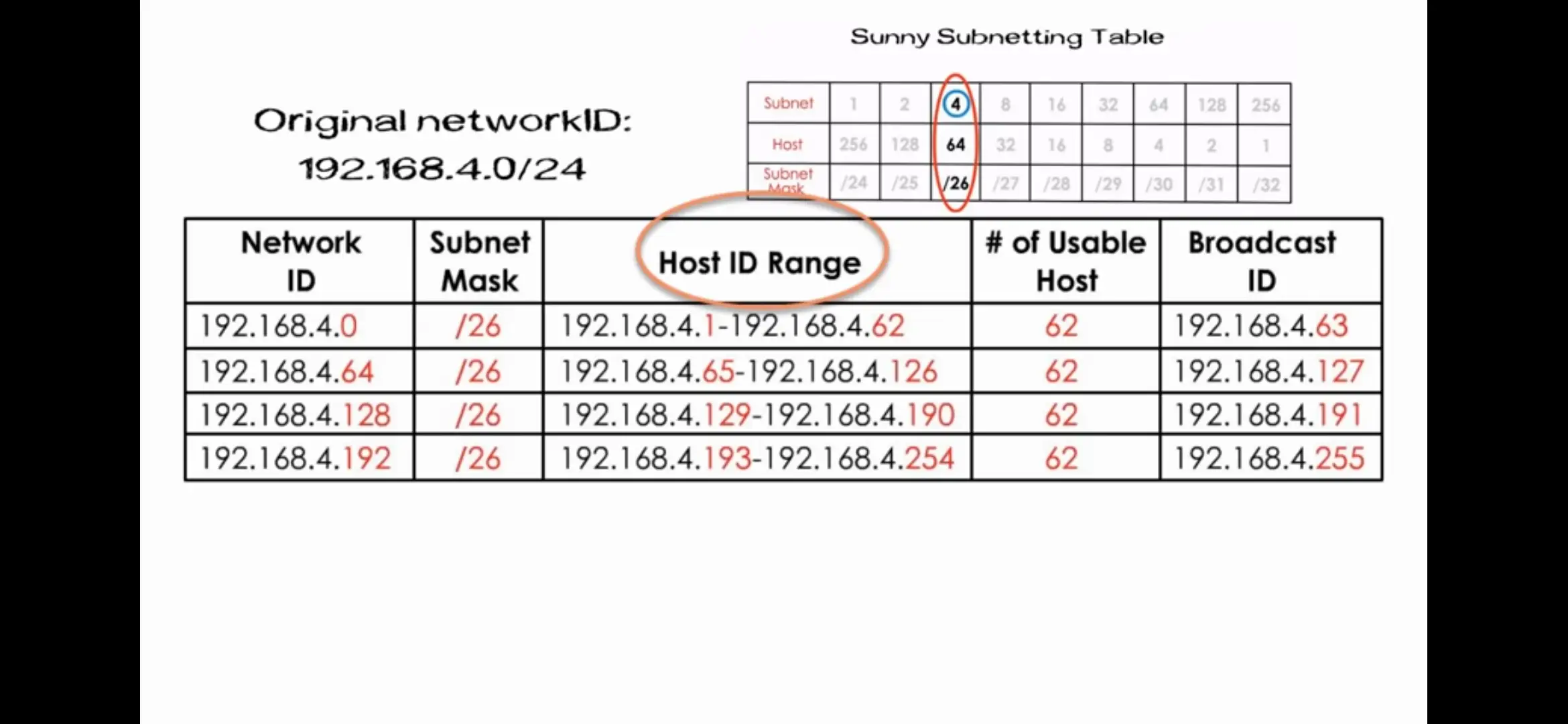
Subnetting
The process of taking a large network and splitting it up into many individual and smaller subnetworks, or subnets.
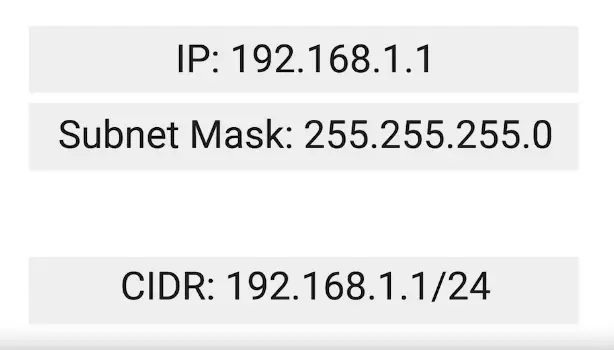
Subnet Masks
32-bits numbers that are normally written out as four octets in decimal.
OR
A way for a computer to use AND operators to determine if an IP address exists on the same network.
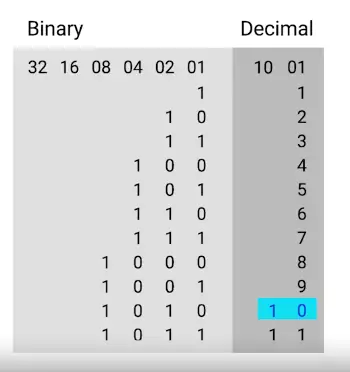
- A single 8-bit number can represent 256 different numbers, or more specifically, the numbers 0-255.
Subnet ID
-
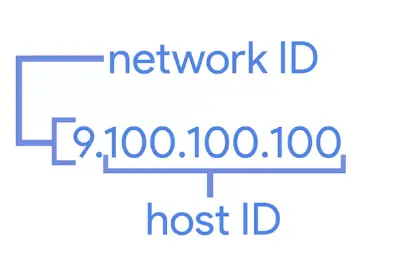
Generally, an IP address consists of Network ID and Host ID
-
In Subnetting world, Host ID is further divided into Subnet ID to identify the subnet mask.
Basic Binary Math
- Two of the most important operators are OR and AND.
- In computer logic, a 1 represents true and a 0 represents false.
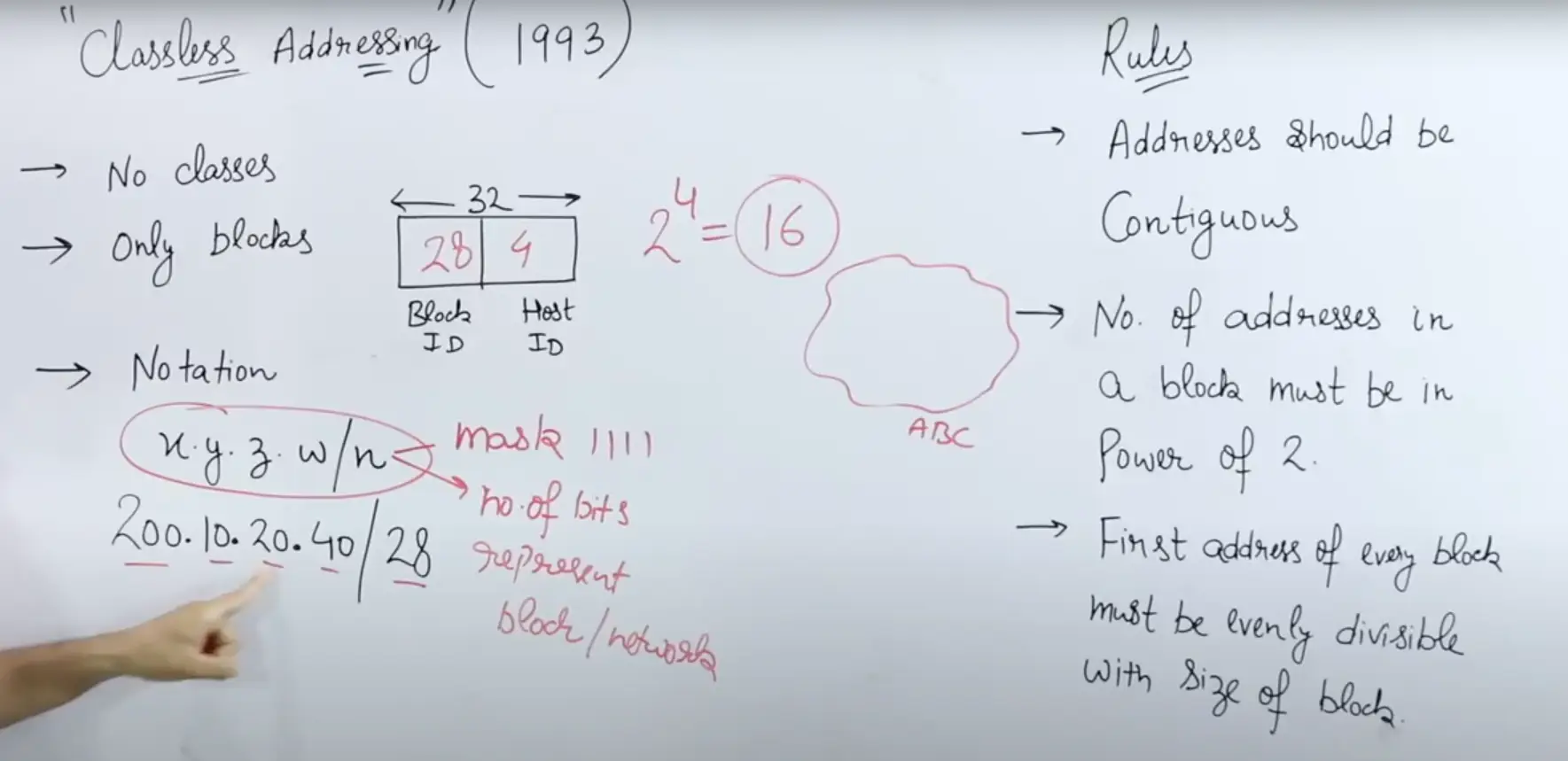
CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)
- Addresses should be continuous
- Number of addresses in a block must be in power of 2
- First address of every block must be evenly divisible with the size of the block
Demarcation point
To describe where one network or system ends and another one begins.
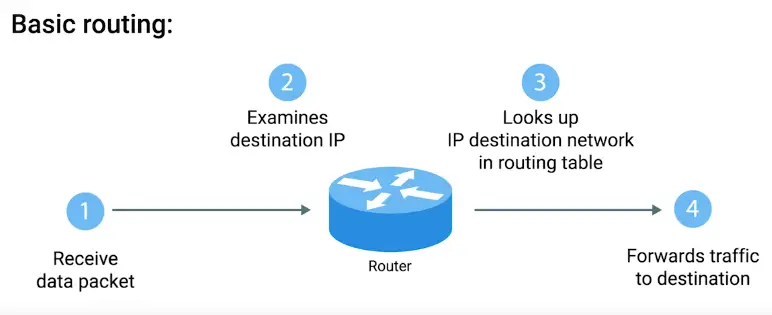
Routing
Basic Routing Concepts
Router
A network device that forwards traffic depending on the destination address of that traffic.
Routing Tables
Routing Protocols
- Routing protocols fall into two main categories: interior gateway protocols and exterior gateway protocols.
- Interior Gateway Protocols
- Link state routing protocols
- distance-vector protocols
Interior Gateway Protocols
Used by routers to share information within a single autonomous system.
Autonomous system
“A collection of networks that all fall under the control of a single network operator.”
In computer science, a list is known as a vector.
Exterior Gateway Protocol
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
“A non-profit organization that helps manage things like IP address allocation.”
- Also, responsible for ASN allocation
Autonomous System Number (ASN)
Numbers assigned to individual autonomous systems.
Non-Routable Address Space
- IPv4 standard doesn’t have enough IP addresses
- There are non-routable address spaces, set aside for internal use only and couldn’t free communicate on the free internet