Subsections of Cloud Computing
Overview of Cloud Computing
Definition and Essential Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing (NIST)
A model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Examples of computing resources include:
- Networks
- Servers
- Applications
- Services
Cloud model
- 5 Essential characteristics
- 3 Deployment models
- 3 Service models
5 Essential characteristics
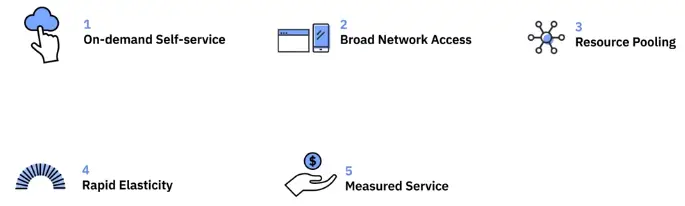

3 Types of cloud deployment models
- Public
- Hybrid
- Private
3 Service models
Three layers in a computing stack:
- Infrastructure (IaaS)
- Platform (PaaS)
- Application (SaaS)
History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
In the 1950s:
-
Large-scale mainframes with high-volume processing power.
-
The practice of time-sharing, or resource pooling, evolved.
-
Multiple users were able to access the same data storage layer and CPU power.
In the 1970s:
-
Virtual Machine (VM)
-
Mainframes to have multiple virtual systems, or virtual machines, on a single physical node
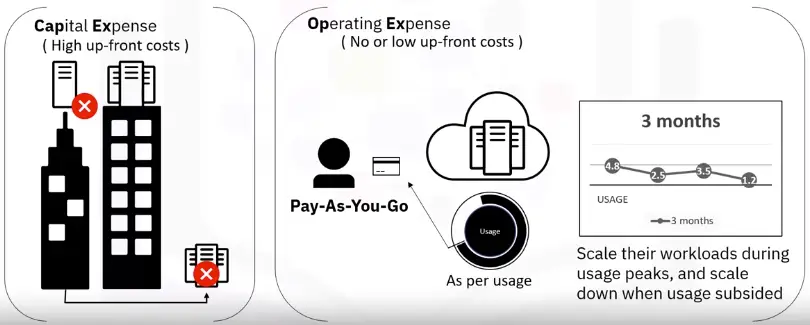
Cloud: Switch from CapEx to OpEx

Key Considerations for Cloud Computing
Key Drivers for moving to cloud


Infrastructure and Workloads
- The cost of building and operating data centers can become astronomical.
- Low initial costs and pay-as-you-go attributes of cloud computing can add up to significant cost savings.
- Organizations need to consider if paying for application access is a more viable option than purchasing off-the-shelf software and subsequently investing in upgrades
Speed and Productivity
- Organizations also need to consider what it means to them to get a new application up and running in ‘x’ hours on the cloud versus a couple of weeks, even months on traditional platforms.
- Also, the person-hour cost efficiencies increases from using cloud dashboards, real-time statistics, and active analytics.
Risk Exposure
- Organizations need to consider the impact of making a wrong decision – their risk exposure.
- Is it safer for an organization to work on a 12-month plan to build, write, test, and release the code if they’re certain about adoption?
- And is it better for them to “try” something new paying-as-you-go rather than making long-term decisions based on little or no trial or adoption?
Benefits of cloud adoption
- Flexibility
- Efficiency
- Strategic Value
Challenges of cloud adoption
- Data security, associated with loss or unavailability of data causing business disruption
- Governance and sovereignty issues
- Legal, regulatory, and compliance issues
- Lack of standardization in how the constantly evolving technologies integrate and interoperate
- Choosing the right deployment and service models to serve specific needs
- Partnering with the right cloud service providers
- Concerns related to business continuity and disaster recovery
Key Cloud Service Providers and Their Services
Future of Cloud Computing


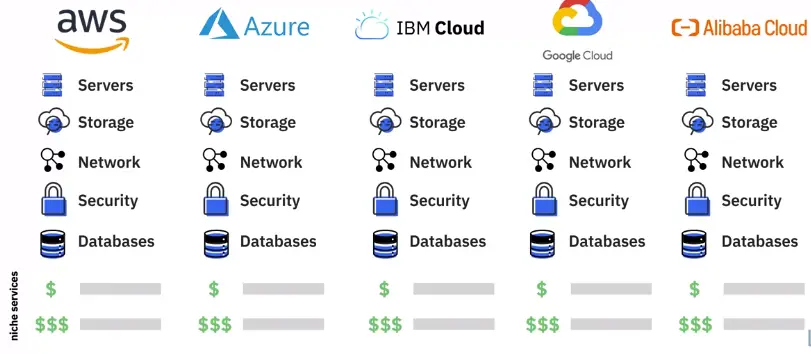
Cloud Service Providers

Alibaba Cloud

Amazon Web Services


IBM Cloud

Microsoft Azure

Oracle Cloud

Salesforce

SAP

Business Case for Cloud Computing
Cloud Adoption – No longer a choice
-
It is no longer a thing of the future
-
Single individual to Global multi-billion dollar enterprise, anybody can access the computing capacity they need on the cloud.
Cloud makes it possible for businesses to:
-
Experiment
-
Fail
-
Learn
Faster than ever before with low risk.
-
Businesses today have greater freedom to change course than to live with the consequences of expensive decisions taken in the past.
-
To remain, competitive, businesses need to be able to respond quickly to marketplace changes.
-
Product lifecycles have shortened, and barriers to entry have become lower.
-
The power, scalability, flexibility, and pay-as-you-go economics of cloud has made it underpinning foundation for digital transformation.
Emerging Technologies Accelerated by Cloud
Internet of Things in the Cloud
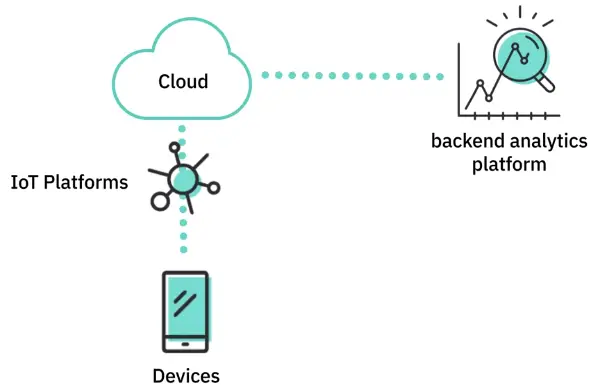

Artificial Intelligence on the Cloud
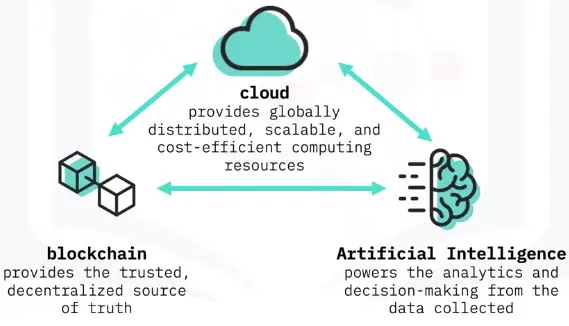
AI, IoT, and the Cloud
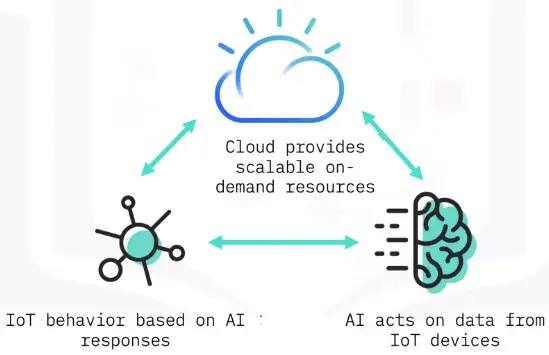

BlockChain and Analytics in the Cloud
Blockchain & Cloud
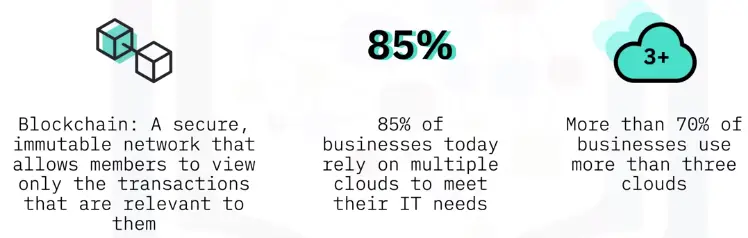

A 3-Way Relationship

Analytics on the Cloud
How can analytics technology leverage the cloud?
- Track trends on social media to predict future events
- Analyze data to build machine learning models in cognitive applications
- Data analytics and predictions maintenance solutions for city infrastructure
Cloud Computing Models
Overview of Cloud Service Models
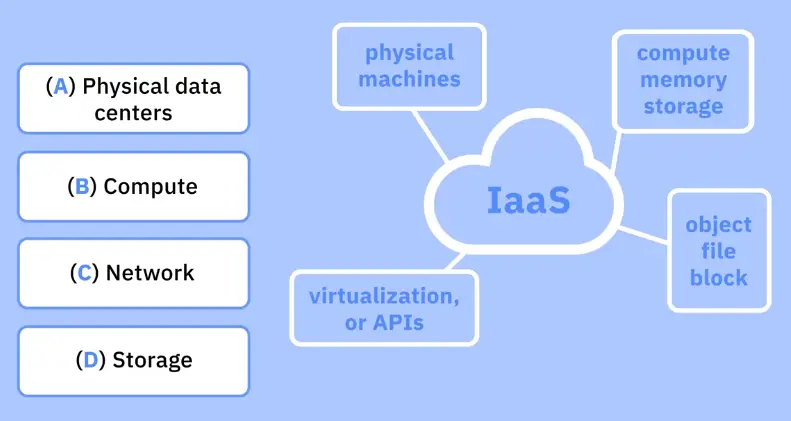
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
It is a form of cloud computing that delivers fundamentals:
-
compute
-
network
-
storage
to consumers on-demand, over the internet, on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The cloud provider hosts the infrastructure components traditionally present in an on-premises data center, as well as the virtualization or hypervisor layer.
IaaS Cloud
The ability to track and monitor the performance and usage of their cloud services and manage disaster recovery.

-
End users don’t interact directly with the physical infrastructure, but experience it as a service provided to them.
-
Comes with supporting services like auto-scaling and load balancing that provide scalability and high performance.
-
Object storage is the most common mode of storage in the cloud, given that it is highly distributed and resilient.

IaaS use cases
Test and Development
- Enable their teams to set up test and development environments faster.
- Helping developers focus more on business logic than infrastructure management.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
- Require a significant amount of technology and staff investment.
- Make applications and data accessible as usual during a disaster or outage.
Faster Deployments and Scaling
- To deploy their web applications faster.
- Scale infrastructure up and down as demand fluctuates.
- To solve complex problems involving millions of variables and calculations
Big Data Analysis
- Patterns, trends, and associations requires a huge amount of processing power.
- Provides the required high-performance computing, but also makes it economically viable.
IaaS Concerns
- Lack of transparency
- Dependency on a third party
PaaS
A cloud computing model that provides a complete application platform to:
- Develop
- Deploy
- Run
- Manage
PaaS Providers Host and Manages
Installation, configuration, operation of application infrastructure:
Essential Characteristics of PaaS
- High level of abstraction
- Eliminate complexity of deploying applications
- Support services and APIs
- Simplify the job of developers
- Run-time environments
- Executes code according to application owner and cloud provider policies
- Rapid deployment mechanisms
- Deploy, run, and scale applications efficiently
- Middleware capabilities
- Support a range of application infrastructure capabilities
Use Cases of PaaS
- API development and management
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Business analytics/intelligence
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Master data management (MDM)
Advantages of PaaS
- Scalability
- Faster time to market
- Greater agility and innovation
PaaS available offerings


Risks of PaaS
- Information security threats
- Dependency on service provider’s infrastructure
- Customer lack control over changes in strategy, service offerings, or tools
SaaS – Software as a Service
A cloud offering that provides access to a service provider’s cloud-based software.
Provider maintains:
SaaS Supports
- Email and Collaboration
- Customer Relationship Management
- Human Resource Management
- Financial Management
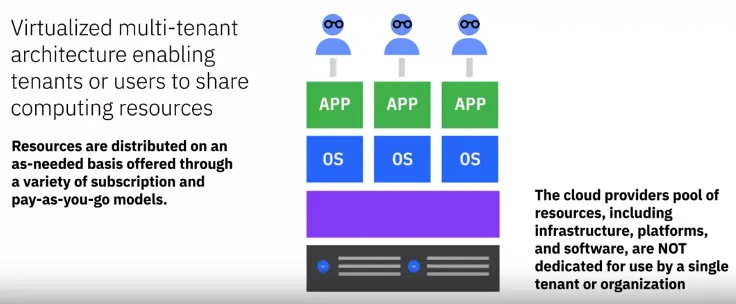
Key Characteristics
- Multi-tenant architecture
- Manage Privileges and Monitor Data
- Security, Compliance, Maintenance
- Customize Applications
- Subscription Model
- Scalable Resources
Key Benefits
- Greatly reduce the time from decision to value
- Increase workforce productivity and efficiency
- Users can access core business apps from anywhere
- Buy and deploy apps in minutes
- Spread out software costs over time
Use Cases for SaaS
Organizations are moving to SaaS to:
-
Reduce on-premise IT infrastructure and capital expenditure
-
Avoid ongoing upgrades, maintenance, and patching
-
Run applications with minimal input
-
Manage websites, marketing, sales, and operations
-
Gain resilience and business continuity of the cloud provider
Trending towards SaaS integration platforms.
SaaS Concerns
- Data ownership and data safety
- Third-party maintains business-critical data
- Needs good internet connection
Deployment Models
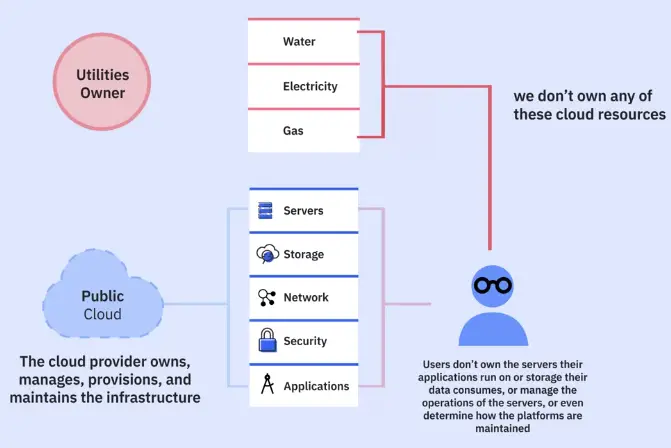
Public Cloud

Public Cloud providers in the market today

Public cloud characteristics

Public cloud benefits


Public cloud concerns


Public cloud use cases
- Building and testing applications, and reducing time-to-market for their products and services.
- Businesses with fluctuating capacity and resourcing needs.
- Build secondary infrastructures for disaster recovery, data protection, and business continuity.
- Cloud storage and data management services for greater accessibility, easy distribution, and backing up their data.
- IT departments are outsourcing the management of less critical and standardized business platforms and applications to public cloud providers.
Private Cloud
“Cloud infrastructure provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization comprising multiple consumers, such as the business units within the organization. It may be owned, managed, and operated by the organization, a third party, or some combination of them, and it may exist on or off premises.”
Internal or External


Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
An external cloud that offers a private, secure, computing environment in a shared public cloud.
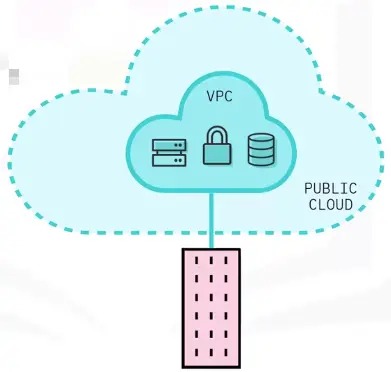

Best of Both Worlds


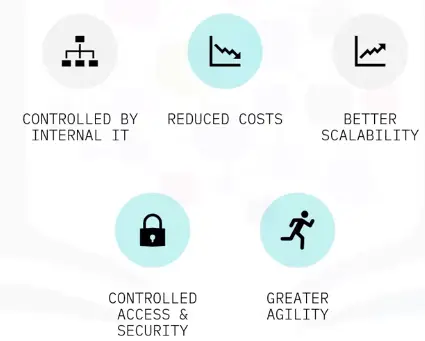
Benefits of Private Clouds

Common Use Cases


Hybrid Cloud
Connects an organization on-premise private cloud and third-party public cloud.
It gives them:
-
Flexibility
-
Workloads move freely
-
Choice of security and regulation features
With proper integration and orchestration between the public and private clouds, you can leverage both clouds for the same workload. For example, you can leverage additional public cloud capacity to accommodate a spike in demand for a private cloud application also known as “cloud bursting”.
The Three Tenets


Types of Hybrid Clouds


Benefits
- Security and compliance
- Scalability and resilience
- Resource optimization
- Cost-saving
- A hybrid cloud lets organizations deploy highly regulated or sensitive workloads in a private cloud while running the less-sensitive workloads on a public cloud.
- Using a hybrid cloud, you can scale up quickly, inexpensively, and even automatically using the public cloud infrastructure, all without impacting the other workloads running on your private cloud.
- Because you’re not locked-in with a specific vendor and also don’t have to make either-or- decisions between the different cloud models, you can make the most cost-efficient use of your infrastructure budget. You can maintain workloads where they are most efficient, spin-up environments using pay-as-you-go in the public cloud, and rapidly adopt new tools as you need them.
Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
- SaaS integration
- Data and AI integration
- Enhancing legacy apps
- VMware migration
Components of Cloud Computing
Overview of Cloud Infrastructure
After choosing the cloud service model and the cloud type offered by vendors, customers need to plan the infrastructure architecture. The infrastructure layer is the foundation of the cloud.
Region
It is a geographic area or location where a cloud provider’s infrastructure is clustered, and may have names like NA South or US East.
Availability Zones
-
Multiple Availability Zones (AZ)
-
Have their own power, cooling, networking resources
-
Isolation of zones improves the cloud’s fault tolerance, decrease latency, and more
-
very high bandwidth connectivity with other AZs, Data Centers and the internet
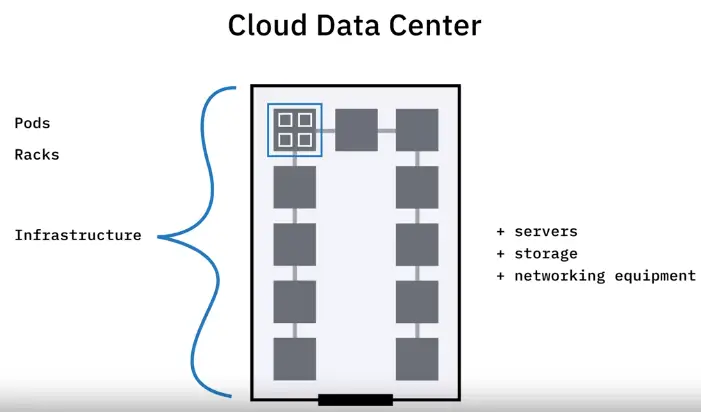

Computing Resources
Cloud providers offer several compute options:
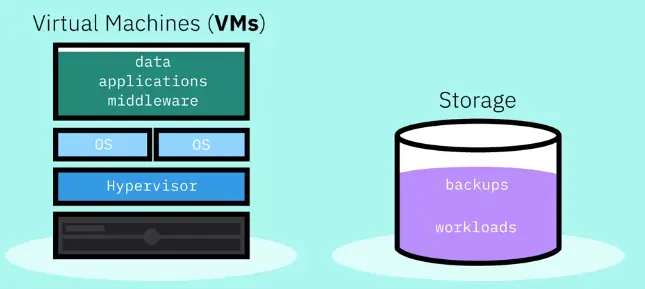
- Virtual Servers (VMs)
- Bare Metal Servers
- Serverless (Abstraction)
Storage
Virtual servers come with their default local storage, but the stored documents are lost as we destroy the servers. Other more persistent options are:
- Traditional Data Centers:
- Block Storage
- File Storage
- Often struggle with scale, performance and distributed characteristics of cloud.
- The most common mode of storage
- It is highly distributed and resilient
Networking
Networking infrastructure in a cloud datacenter include traditional networking hardware like:
-
routers
-
switches
For users of the Cloud, the Cloud providers have Software Defined Networking (SDN), which allows for easier networking:
-
provisioning
-
configuration
-
management
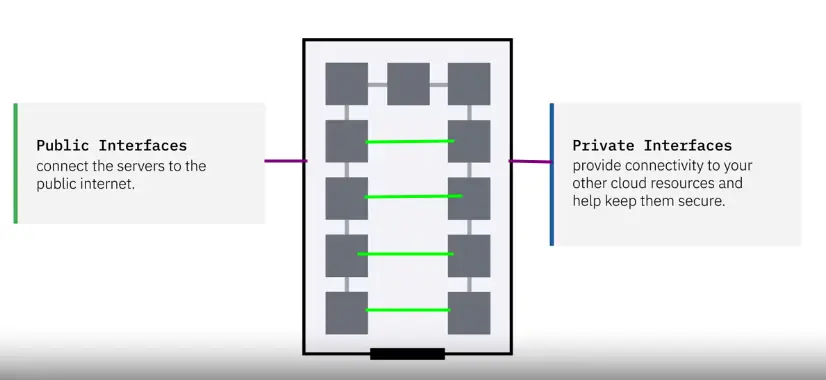

Networking interfaces in the cloud need:
-
IP address
-
Subnets
It is even more important to configure which network traffic and users can access your resources:
-
Security Groups
-
ACLs
-
VLANs
-
VPCs
-
VPNs
Some traditional hardware appliances:
-
firewalls
-
load balancers
-
gateways
-
traffic analyzers
Another networking capability provided by the Cloud Providers is:
-
CDNs
Types of Virtual Machines
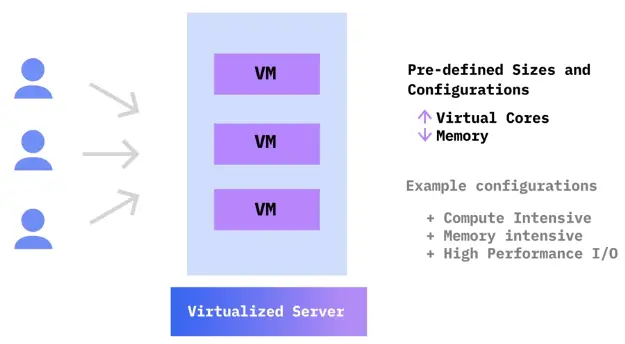
Shared or Public Cloud VMs

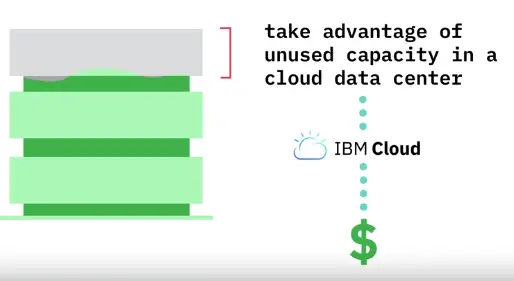
Transient or Spot VMs
-
The Cloud provider can choose to de-provision them at any time and reclaim the resources
These VMs are great for:
-
Non-production
-
Testing and developing applications
-
Running stateless workloads, testing scalability
-
Running big data and HPC workloads at a low cost

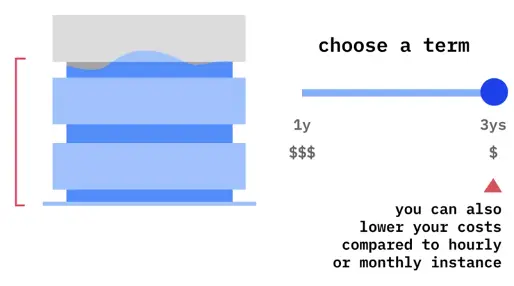
Reserved virtual server instances
-
Reserve capacity and guarantee resources for future deployments
-
If you exceed your reserved capacity, complement it with hourly or monthly VMs
Note: Not all predefined VMs families or configuration may be available as reserved.

Dedicated Hosts
- Single tenant isolation
- Specify the data center and pod
- This allows for maximum control over workload placement
- Used for meeting compliance and regulatory requirements or licensing terms
A bare metal server is a single-tenant, dedicated physical server. In other words, it’s dedicated to a single customer.
- Cloud Provider manages the server up to the OS.
- The Customer is responsible for administering and managing everything else on the server.
- Preconfigured by the cloud provider
- Custom-configured as per customer specifications
-
Processors
-
RAM
-
Hard drives
-
Specialized components
-
The OS
Add GPUs:
- Accelerating scientific computation
- Data analytics
- Rendering professional grade virtualized graphics
Characteristics
- Can take longer to provision
- Minutes to hours
- More expensive than VMs
- Only offered by some cloud providers
Workloads
-
Fully customizable/ demanding environments
-
Dedicated or long-term usage
-
High Performance Computing
-
Highly secure / isolated environments

| Bare Metal |
Virtual Servers |
| Work best for: CPU and I/O intensive workloads |
Rapidly provisioned |
| Excel with the highest performance and security |
|
| Satisfy strict compliance requirements |
Provide an elastic and scalable environment |
| Offer complete flexibility, control, and transparency |
|
| Come with added management and operational over head |
Low cost to use |
Secure Networking in Cloud
Networking in Cloud vs. On Premise
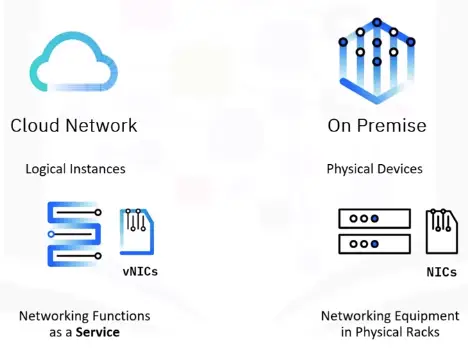

To create a network in cloud:
Direct Connectivity


Building a Cloud
It entails creating a set of logical constructs that deliver networking functionality akin to data center networks for securing environments and ensuring high performing business applications.
Containers
Containers are an executable unit of software in which application code is packaged, along with its libraries and dependencies, in common ways so that it can be run anywhere—desktops, traditional IT, or the cloud. Containers are lighter weight and consume fewer resources than Virtual Machines.
- Containers streamline development and deployment of cloud native applications
- Fast
- Portable
- Secure
Cloud Storage and Content Delivery Networks
Basics of Storage on the Cloud
File Storage
Like Direct attached:
-
Attached to a compute node to store data
Unlike Direct attached:
-
Less expensive
-
More resilient to failure
-
Less disk management and maintenance for user
-
Provision much larger amounts of Storage
File storage is mounted from remote storage appliances:


-
Resilient to failure
-
Offer Encryption
-
Managed by service provider
File storage is mounted on compute nodes via Ethernet networks:


Multiple Compute Nodes
- File storage can be mounted onto more than one compute node
- Common Workloads:
- Low cost database storage
IOPS
Input/Output Operations Per Second – the speed at which disks can write and read data.
- Higher IOPS value = faster speed of underlying disk
- Higher IOPS = higher costs
- Low IOPS value can become a bottleneck
Block Storage
What is Block Storage?
Block storage breaks files into chunks (or block) of data.
-
Stores each block separately under a unique address.
-
Must be attached to a compute node before it can be utilized.
Advantages:
-
Mounted from remote storage appliances
-
Extremely resilient to failure
-
Data is more secure
Mounted as a volume to compute nodes using a dedicated network of optical fibers:
-
Signals move at the speed of light
-
Higher price-point
-
Perfect for workloads that need low-latency
-
Consistent high speed
-
Databases and mail servers
-
Not suitable for shared storage between multiple servers
IOPS
For block storage, as it is for file storage, you need to take the IOPS capacity of the storage into account:
- Specify IOPS characteristics
- Adjust the IOPS as needed
- Depending on requirements and usage behavior
Common Attributes of File and Block Storage
- Block and File Storage is taken from appliances which are maintained by the service provider
- Both are highly available and resilient
- Often include data encryption at rest and in transit
Differences: File Storage vs. Block Storage
| File Storage |
Block Storage |
| Attached via Ethernet network |
Attached via high-speed fiber network |
| Speeds vary, based on load |
Only attach to one node at a time |
| Can attach to multiple computer nodes at once |
|
| Good for file share where: |
|
| 1) Fast connectivity isn’t required |
Good for applications that need: |
| 2) Cost is a factor |
1) Consistent fast access to disk |
Remember: Consider workload IOPS requirements for both storage types.
Object Storage
- Object storage can be used without connecting to a particular compute node to use it:

- Object storage is less expensive than other cloud storage options
- The most important thing to note about Object Storage is that it’s effectively infinite
- With Object Storage, you just consume the storage you need and pay per gigabyte cost for what you use.
When to use Object Storage:
- Good for large amounts of unstructured data
- Data is not stored in any kind of hierarchical folder or directory structure
Object Storage Buckets
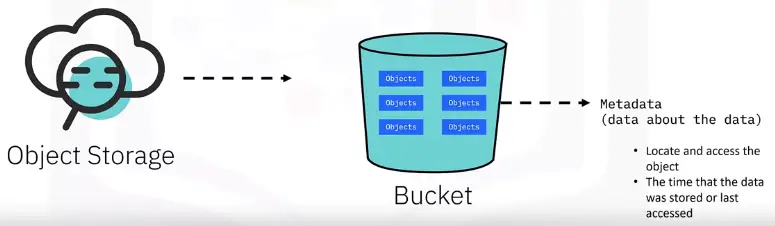



Managed by Service Provider

Object Storage – Resilience Options
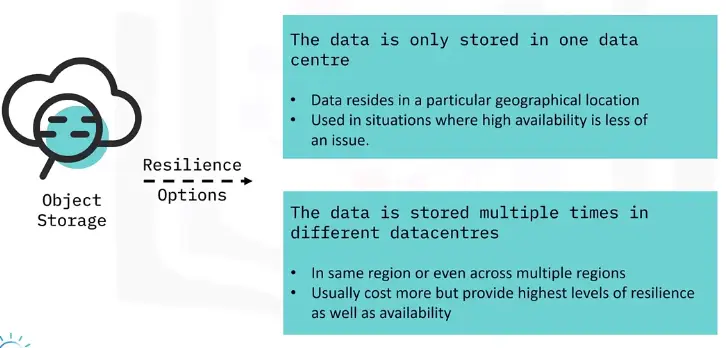

Object Storage – Use Cases
- Any Data which is static and where fast read and write speeds are not necessary
Object Storage – Tiers and APIs
Object Storage Tiers
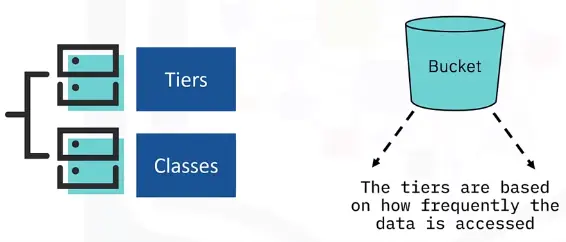

Standard Tier
- Store objects that are frequently accessed
- Highest per gigabyte cost
Vault/Archive Tier
- Store objects that are accessed once or twice a month
- Low storage cost
Cold Vault Tier
- Store data that is typically accessed once or twice a year
- Costs just a fraction of a US cent per/GB/month
Automatic archiving rules
- Automatic archiving rules for your data
- Automatically be moved to a cheaper storage tier if object isn’t accessed for long
Object Storage – Speed
- Doesn’t come with IOPS options
- Slower than file or block storage
- Data in ‘cold vault’ buckets, can take hours for retrieval
- Object storage not suitable for fast access to files.
Object Storage – Costs
-
Object Storage is priced per/GB
-
Other costs related to retrieval of the data
e.g., Higher access costs for cold vault tiers
Ensure data is stored in correct tier based on frequency of access.
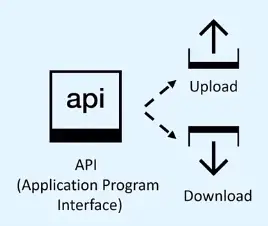
Application Programming Interface, or API
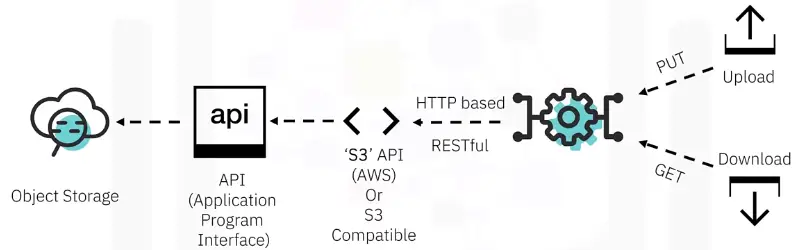

Object Storage – Backup solutions
- Effective solution for Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Replacement for offsite backups
- Many backup solutions come with built-in options for Object Storage on Cloud
- More efficient than tape backups for geographic redundancy
CDN – Content Delivery Network
- Accelerates content delivery to users of the websites, by caching the content in data centers near their locations.
- Makes websites faster.
- Reduction in load on servers
- Increase uptime
- Security through obscurity
Hybrid Multi-Cloud, Microservices, and Serverless
Hybrid Multi-cloud
A computing environment that connects an organization’s on-premise private cloud and third-party public cloud into a single infrastructure for running the organization’s applications.
Hybrid Multicloud use cases
- Cloud scaling
- Composite cloud
- Modernization
- Data and AI
- Prevent lock-in to a particular cloud vendor and having a flexibility to move to a new provider of choice
Microservices
Microservices architecture:
- Single application
- coupled and independently deployable smaller components or services
- These services typically have their own stack running on their own containers.
- They communicate with one another over a combination of:
- APIs
- Even streaming
- Message brokers
What this means for businesses is:
- Multiple developers working independently
- Different stacks and runtime environments
- Independent scaling
Serverless Computing
Offloads responsibility for common infrastructure management tasks such as:
- Scaling
- Scheduling
- Patching
- Provisioning
Key attributes
Attributes that distinguish serverless computing from other compute models:
- No provisioning of servers and runtimes
- Runs code on-demand, scaling as needed
- Pay only when invoked and used
i.e., not when underlying computer resources are idle.
Serverless
- Abstracts the infrastructure away from developers
- Code executed as individual functions
- No prior execution context is required
A Scenario
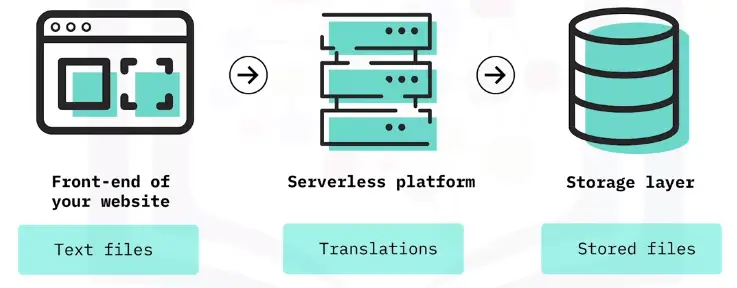

Serverless computing services
- IBM Cloud Functions
- AWS Lambda
- Microsoft Azure Functions
Determining Fit with Serverless
-
Evaluate application characteristics
-
Ensure that the application is aligned to serverless architecture patterns
Applications that qualify for a serverless architecture include:
-
Short-running stateless functions
-
Seasonal workloads
-
Production volumetric data
-
Event-based processing
-
Stateless microservices
Use Cases
Serverless architecture are well-suited for use cases around:
-
Data and event processing
-
IoT
-
Microservices
-
Mobile backends
Serverless is well-suited to working with:
-
Text
-
Audio
-
Image
-
Video
Tasks:
-
Data enrichment
-
Transformation
-
Validation and cleansing
-
PDF processing
-
Audio normalization
-
Thumbnail generation
-
Video transcoding
-
Data search and processing
-
Genome processing
Data Streams:
-
Business
-
IoT sensor data
-
Log data
-
Financial market data
Challenges

Vendor Dependent Capabilities
-
Authentication
-
Scaling
-
Monitoring
-
Configuration management

Cloud Native Applications, DevOps, and Application Modernization
Cloud Native Applications
- Developed to work only in the cloud environment
- Refactored and reconfigured with cloud native principles
Development Principles
Whether creating a new cloud native application or modernizing an existing application:
- Microservices Architecture
- Rely on Containers
- Adopt Agile Methods
Benefits
- Innovation
- Agility
- Commoditization
DevOps on the Cloud
What is DevOps?
Dev Teams:
The DevOps Approach
It applies agile and lean thinking principles to all stakeholders in an organization who develop, operate, or benefit from the business’s software systems, including customers, suppliers, partners. By extending lean principles across the software supply chain, DevOps capabilities improve productivity through accelerated customer feedback cycles, unified measurements and collaboration across an enterprise, and reduced overhead, duplication, and rework.
Using the DevOps approach:
- Developers can produce software in short iterations
- A continuous delivery schedule of new features and bug fixes in rapid cycles
- Businesses can seize market opportunities
- Accelerated customer feedback into products
DevOps Process
-
Continuous Delivery
-
Continuous Integration
-
Continuous Deployment
-
Continuous Monitoring
-
Delivery Pipeline

DevOps and Cloud
With its near limitless compute power and available data and application services, cloud computing platforms come with their own risks and challenges, which can be overcome by DevOps:
-
Tools
-
Practices
-
Processes
DevOps provides the following solutions to cloud’s complexities:
-
Automated provisioning and installation
-
Continuous integration and deployment pipelines
-
Define how people work together and collaborate
-
Test in low-cost, production-like environments
-
Recover from disasters by rebuilding systems quickly and reliably
Application Modernization
Enterprise Applications
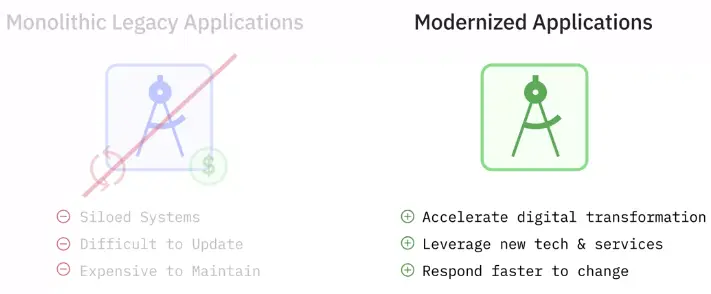

Application Modernization
Architecture: Monoliths > SOA (Service Oriented Architecture) > Microservices
Infrastructure: Physical servers > VM > Cloud
Delivery: Waterfall > Agile > DevOps
Cloud Security, Monitoring, Case Studies, Jobs
What is Cloud Security
The security in context of cloud is a shared responsibility of:
-
User
-
Cloud Provider
-
Protect data
-
Manage access
SEC DevOps
-
Secure Design
Identity and Access Management
Biggest cloud security concerns are:
-
Data Loss and Leakage
-
Unauthorized Access
-
Insecure Interfaces and APIs
Identity and Access Management are:
-
First line of defense
-
Authenticate and authorize users
-
Provide user-specific access
Main types of users
A comprehensive security strategy needs to encompass the security needs of a wide audience:
-
Organizational users
-
Internet and social-based users
-
Third-party business partner organizations
-
Vendors
There are three main type of users:
-
Administrative users
-
Developer users
-
Application users
Administrative Users
Administrators | Operators | Mangers
roles that typically create, update, and delete application and instances, and also need insight into their team members’ activities.
An attacker with administrative access could:
- Steal data from databases
- Deploy malicious applications
- Deface or destroy existing applications
Developer Users
Application developers | Platform developers | Application publishers
Can:
- Read sensitive information
- Create applications
- Update applications
- Delete applications
Application Users
Users of the cloud-hosted applications
Authentication and User Identity
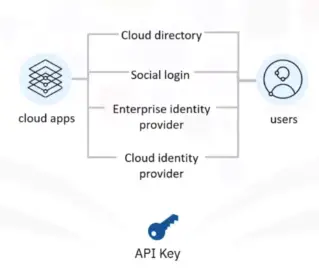

Multifactor authentication
It is used to combat identity theft by adding another level of authentication for application users.
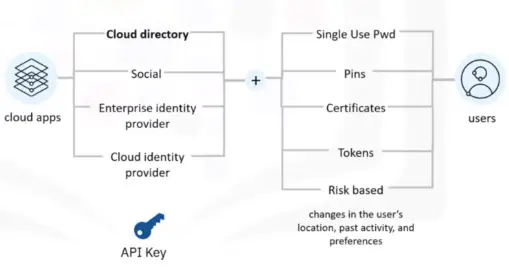

Cloud Directory Services
They are used to securely manage user profiles and their associated credentials and password policy inside a cloud environment.
- Applications hosted on the cloud do not need to use their own user repository
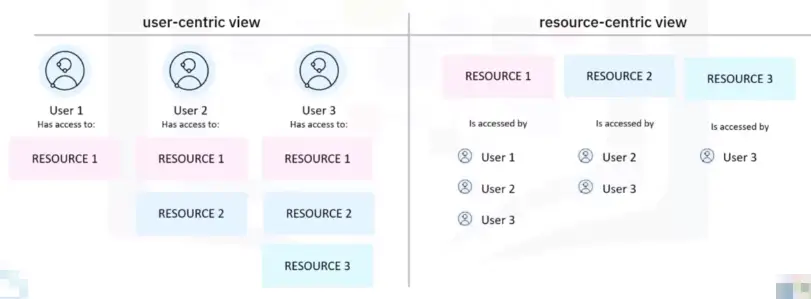
Reporting
It helps provide a user-centric view of access to resources or a resource-centric view of access by users:
-
which users can access which resources
-
changes in user access rights
-
access methods used by each user

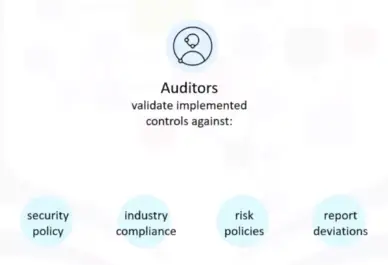
Audit and Compliance
Critical service within identity and access management framework, both for cloud provider, and cloud consumer.

User and service access management
It enables cloud application/service owners to provision and de-provision:
Streamline access control based on:
- Role
- Organization
- Access policies
Mitigating Risks
Some of the controls that can help secure these sensitive accounts include:
- Provisioning users by specifying roles on resources for each user
- Password policies that control the usage of special characters, minimum password lengths, and other similar settings
- Multifactor authentication like time-based one-time passwords
- Immediate provisioning of access when users leave or change roles
Access Groups
A group of users and service IDs created so that the same access can be assigned to all entities within the group with one or more access policies.
Access Policies
Access policies define how users, service IDs, and access groups in the account are given permission to access account resources.


Access Group Benefits
Cloud Encryption
Encryption
It plays a key role on cloud, and is often referred to as the last line of defense, in a layered security model.
- Encrypts Data
- Data Access Control
- Key management
- Certificate management
Definition
Scrambling data in a way that makes it illegible.
Encryption Algorithm:
Defines rules by which data will be transformed
Decryption Key:
Defines how encrypted data will be transformed back to legible data.
It makes sure:
- Only authorized users have access to sensitive data.
- When accessed without authorization, data is unreadable and meaningless.
Cloud Encryption Services
- Can be limited to encryption of data that is identified as sensitive, or
- end-to-end encryption of all data uploaded to the cloud
Data Protection States
Encryption at Rest:
- Protects stored data
- Multiple encryption options:
- Protects data while transmitting
- Includes encrypting before transmission
- Authenticates endpoints
- Decrypts data on arrival
- Protects data in use in memory
- Allows computations to be performed on encrypted text without decryption
Client or Server-side Encryption
Cloud storage encryption could be server-side or client-side.
Server-side:
-
Create and manage your own encryption keys, or
-
Generate and manage keys on cloud
Client-side:
-
Occurs before data is sent to cloud
-
Cloud providers cannot decrypt hosted data
There is a need to implement a singular data protection strategy across an enterprise’s on-premise, hybrid, and multi-cloud deployments.
Multi-Cloud Data Encryption
Features:
-
Data access management
-
Integrated key management
-
Sophisticated encryption
Multi-cloud encryption console:
-
Define and manage access policies
-
Create, rotate, and manage keys
-
Aggregate access logs
Key Management
Encryption doesn’t eliminate security risk.
- It separates the security risk from the data itself.
- Keys need to be managed and protected against threats.
Key Management Services
They enable customers to:
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest
- Easily create and manage the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys
- Protect data from cloud service providers
Key Management Best Practices
- Storing encryption keys separately from the encrypted data
- Taking key backups offsite and auditing them regularly
- Refreshing the keys periodically
- Implementing multifactor authentication for both the master and recovery keys
Cloud Monitoring Basics and Benefits
Cloud Monitoring Solutions
Monitoring performance across an entire stack of applications and services can be time-consuming and draining on internal resources.
Cloud Monitoring Assessment


Cloud Monitoring Features
Cloud monitoring includes:
Cloud Monitoring Helps to:
- Accelerate the diagnosis and resolution of performance incidents
- Control the cost of your monitoring infrastructure
- Mitigate the impact of abnormal situations with proactive notifications
- Get critical Kubernetes and container insights for dynamic microservice monitoring
- Troubleshoot your applications and infrastructure
Cloud Monitoring Solutions Provide:
- Data in real-time with round the clock monitoring of VMs, services, databases, apps
- Multilayer visibility into application, user, and file access behavior across all apps
- Advanced reporting and auditing capabilities for ensuring regulatory standards
- Large-scale performance monitoring integrations across multicloud and hybrid cloud
Cloud Monitoring Categories
Infrastructure
-
Help identify minor and large-scale failures
- So that developers can take corrective action
Database
-
Help track processes, queries, and availability of services
-
Help improve user experience
-
Meet app and user SLAs
- Minimize downtime and lower operational costs
Cloud Monitoring Best Practices
To get the most benefit from your cloud-based deployments, you can follow some standard cloud monitoring best practices.
- Leverage end-user experience monitoring solutions
- Move all aspects of infrastructure under one monitoring platform
- Use monitoring tools that help track usage and cost
- Increase cloud monitoring automation
- Simulate outages and breach scenarios
Cloud monitoring needs to be a priority for organizations looking to leverage the benefits of cloud technologies.
Case Studies and Jobs
Case Studies in Different Industry Verticals
- The Weather Company migrating to the cloud to reliably deliver critical weather data at high speed, especially during major weather events such as hurricanes and tornadoes
- American Airlines, using the cloud platform and technologies to deliver digital self-service tools and customer value more rapidly across its enterprise
- Cementos Pacasmayo, achieving operational excellence and insight to help drive strategic transformation and reach new markets using cloud services
- Welch choosing cloud storage to drive business value from hybrid cloud
- Liquid Power using cloud-based SAP applications to fuel business growth
Career Opportunities and Job Roles in Cloud Computing

