Technical Support Skills and Opportunities
Technical Support Soft Skills
What are soft skills?
- Positive behaviors and attitudes
- Effectively communicate, collaborate, and manage
- Actively listen to clients
- Work with others to resolve problems
- Diffuse stressful situations
Soft skills
- Customer service mindset
- Communication
- Organization
- Leadership
- Problem-solving
- Flexible and adaptable
Positive behaviors and attitudes
- Knowledge of technology is one part
- Work with others and manage social situations
- Positive behaviors and attitudes
- Effectively communicate, collaborate, and manage conflict
Set yourself up for success
- Use your soft skills
- Ask questions
- Take good notes
- Stay organized
- Say “I don’t know” and “I’ll find out”
Customer Support mindset
- Empathetic
- Customer-centered
- Patient
Learn to improve
- Document your notes as you work
- Read suggestions and notes from supervisors
- Learn techniques to help you withstand pressure and reduce stress
Experienced background
- Lack of work experience does not mean that you lack interest in technology
- Use your passion for technology to boost your self-confidence
- Positive behaviors and attitudes
- Be willing to level-up your soft skills
Soft-skills tune-up
- Additional online courses
- Podcasts, audiobooks
- Peers and social groups
Basics of Technical Skills
The job interview


Basic programming and coding
- Machine code and source code
- Compiled programming and interpreted programming languages
- Programming languages like C, Java, HTML, Python, and JavaScript
- Basic-level coding
Computers and operating systems
- Basic knowledge of android, iOS, Windows, Linux, macOS is necessary.
SQL and NoSQL basics
- Basic knowledge of both
- Differences of SQL and NoSQL
- SQL queries retrieve information
- NoSQL databases are nonrelational databases with unstructured data
- Technical support services for databases
- Database application services, management, security, backups, updates, and optimization
Analyze application logs
- View information about events that have occurred in an application
- Read and analyze application logs
- Track information about the application
- Includes timestamps for tracking issues
- Logs levels of issues with labels
Server knowledge
- Understand servers
- Settings up and configuring servers
- Updating server software
- Monitoring and maintaining servers
- Maximizing uptime
- Managing virtual servers
Support ticket workflow
- Track and manage client questions and issues
- Zendesk, Jira, and LiveAgent
- Similar workflow for most ticketing systems
Using knowledge base
- Knowledge base skills
- A collection of a group’s knowledge
New hardware and applications
- Trying new hardware and applications
- Interest in emerging technology
- VMs
- VPNs
- Network security
- IT infrastructure monitoring software
- Enterprise hardware
What is the purpose of a performance evaluation?
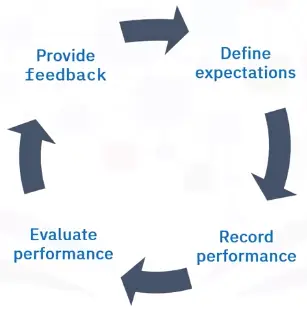

What you should expect?
- Accomplishing responsibilities
- Possess technical knowledge and skills necessary to perform your job
- Understand company policies and procedures
- Complete required records, documents, and tickets
- Decision-making
- Evaluate issues
- Work on your own
- Recognize problems
- Make decisions
- Productivity
- Complete tasks in a timely and efficient manner
- Work according to instructions
- Ask for help, when needed
- Customer service
- Strong commitment to customers
- Work towards a solution
- Call recordings
- Customer ratings
- Time-to-resolve measurements
- First-contact resolution and contacts per customer
- Average number of tickets handled
- Work attitude
- Positive attitude for work and responsibilities
- Effective working relationships with others
- Positive attitude toward suggestions
- Communication skills
- You write clearly, and effectively
- You understand written and spoken communication
- Goal achievements
- Your new certifications and skills
- Achievement of professional goals
- How you have improved
- Your role performance
- Recognition for your accomplishments
- Share your “good job” moments
- Discuss goals and ways to meet goals
- Provide opportunities for advancement
Career Paths and Progression in Technical Support
Technical Support entry-level roles
- IT support specialist
- IT technician
- Help Desk technician
- Desktop Support Specialist
- Field Service Technician
Skills for entry-level roles
- Access data and share with those who need it
- Actively listen to clients and their description of computer-related issues
- Ask questions to determine the problem
- Guide customers through steps to resolve problems
- Train users on new computers and software
- Note changes, updates, and issues
- Share information with other team members and managers
Experience for entry-level roles
- IT experience or a degree not required
- Customer service experience is beneficial
- Knowledge of technology is a plus
- Increase your chances of getting a better job
- Professional certificates
- A computer science or related degree
Technical support mid-level roles
- Help desk analyst
- Technical support specialist
- Tier II Support
Skills for mid-level roles
- Test and maintain equipment and software
- Try out new systems and programs
- Communicate with clients about technology use
- Train users on how to use new hardware and applications
- Communicate on proper use of technology
- Train new technical support team
Experience for mid-level roles
- Technical support specialist level 2
- 1 to 3 years of experience
- With on-the-job training
- Certifications, Cisco, Microsoft, and CompTIA, like A+, Network+, Security+
- Technical support specialist level 3
- 3 to 5 years of experience
- Advanced on-the-job training
- Certifications similar to level 2
Technical support upper-level roles
- Technical support lead or manager
- IT support team lead
- Field engineer supervisor
Skills for upper-level roles
- Manage systems and capabilities
- Research and explore new systems, software, and processes
- Train users on standard usage practices for hardware and software
- Manage ongoing issues in projects
- Communicate changes in policies to organization management
- Manage and train teams
Experience for upper-level roles
- On-the-job training in leadership
- 5 or more years of experience
- ITIL, SixSigma, and relevant certifications
Technical Support Paths
- Use technical support experience to switch to other IT roles
- Develop cross-skills you can apply to other roles
- Consider tasks and responsibilities you enjoy
- Interview for roles that want to know more about
Cross-skills and up-skill paths
- Use cross-skills you learn on the job to move to better roles
- Level-up skills to promote to more roles
Cross-skill and up-skill roles
- Network Administrator
- Network Security Analyst
- Database Administrator
- Cloud Developer
- QA Engineer
- Software Developer
Industry Certifications for Technical Support
What are industry certifications?
- Certify skills meet industry standards
- Confirm understanding of strategies and concepts
- Validate knowledge about information technology (IT)
- Certify that starting skill requirements are met
- Show specialization in the field
Certifications
- Certifications for starting a career in technical support
- CompTIA, Microsoft, Apple, ITIL Foundation, and Cisco
CompTIA IT Fundamentals (ITF+)
- For starting in IT
- Demonstrates basic IT knowledge and skills
CompTIA A+ for progressing in technical support
Demonstrates mastery of:
- Hardware
- Software troubleshooting
- Networking
- Operating systems
- Device and network troubleshooting
- Security for devices and networks
- Mobile devices Virtualization and Cloud computing
- Operational procedures
CompTIA Network+
- Networking path
- Demonstrating skills for troubleshooting, configuring, and managing networks
Microsoft 365 Certified: Fundamentals
- Microsoft role-based and specialty-based certifications
Apple Certified Support Professional (ACSP)
- For technical support for Mac users
- macOS, troubleshooting, and support
ITIL Foundation certifications
- Start at support center courses
- Develop skills in supporting customers, IT role functions, and troubleshooting methods
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA)
- Demonstrate knowledge of networking
- Highlights skills in administering network maintenance, creating secure network access, and improving network connectivity
- Certification are not required
- Begin by studying for certifications
- Some employers offer assistance
- Ask about certification opportunities
Ticketing Systems
What are ticketing systems?
- A support ticket records the interaction between a customer and a service representative
- Documents issues and their progress/resolution
- Ticket also called Issue, Case, Incident, etc.
- Support tickets are managed by a ticketing system
- These systems may also be called:
- Helpdesk software
- Customer support software
- Ticketing software/app
- Case Management System or Customer Care Management System
What is a ticketing system?
- Software used to systematically document, track, manage, and resolve customer issues.
- Creation of tickets
- Central data hub
What a ticketing system provides
- Automation
- Collaboration
- Integration
- Channels
- Reporting
Lifecycle of a ticket
- Create a ticket
- Assign and Start ticket issue
- Resolve issue
- Close ticket
Features and Benefits of Ticketing Systems
Common features
- Omnichannel support
- Email
- Social media
- Live chat
- Phone
- Ticket routing
- Ticket categorization and tagging
- Categorization
- Tagging
- Routing
- Ticket status
- Tracking and measurement
- Knowledge base management
- Automation
- Helps get to the right person at the right time
- Automation:
- Assigning tickets
- Sending responses
- Escalate issues
- Pulling customer data
- Reduce time spent on repetitive tasks
- Help make agents more engaged and productive
Popular Ticketing Systems
What to look for
- Agent productivity
- Customer interactions
- Metrics
- Continuous improvement
- Collaboration
Types of ticketing systems
- Cloud based
- Self hosted
- Open source
- Enterprise
Cloud based systems
Benefits
- Easier to set up and maintain
- Scalable
- Availability
Concerns
- Vendor must resolve issues
- Internet connection always required
- Limited customization
Self-hosted systems
Benefits
- Complete control of data and security
- More customizable
Concerns
- Initial investment
- Server maintenance
- Updates and fixes
- Backups
Open-source systems
Benefits
- Free or mostly free
- Highly customizable
- Developer community
Concerns
- Knowledgeable developers
- Long installation timeline
- In house updating and maintenance
Enterprise systems
Benefits
- Asset management and reporting
- Support 24 hours a day
- Highly customizable
Concerns
- Expensive
- Higher level of training
Popular ticketing systems
- Zendesk
- Jira Service Desk
- Freshdesk
- LiveAgent
- ServiceNow
Common features
- Omnichannel support
- Automation
- Collaboration
- Knowledge Base
- Subscription Based
- Free trials
Zendesk
- Cloud based
- Pre-built Integrations
- Collaboration
- Knowledge base
- Live chat/chatbots
- Macros
- Expensive
Jira Service Desk
- Cloud or self-hosted
- Built on Jira
- Expandable
- External knowledge base
- Limited chat
- Automation
Freshdesk
- Cloud based
- Custom ticket views
- AI powered chatbots
- Freshworks academy
- Moderate pricing
LiveAgent
- Cloud based
- Emphasized live chat
- Advanced integration
- Chat widget
- Unlimited email addresses
- Moderate pricing
ServiceNow
- Cloud based
- ITSM Approach
- Repeatable workflow
- Advanced integration
- Integrated mobile
- Request quote
Troubleshooting
CompTIA troubleshooting model steps
- Identify the problem
- Gather information
- Question users
- Identify symptoms
- Determine if anything has changed
- Duplicate the problem
- Approach multiple problems individually
- Research the knowledge base/Internet
- Establish a theory of probable cause
- Question the obvious (Is the printer turned on?)
- Consider more than one approach
- Test the theory to determine the cause
- Are you successful?
- More research and testing may be required
- Establish a plan of action
- Some fixes may require reboots or downtime
- May require downloading software or patches
- Test in staging environment if available
- Back up data
- May require approval
- Implement the solution or escalate
- Run scripts
- Update systems or software
- Update configuration files
- Change firewall settings
- Verify full system functionality and implement preventive measures
- Ask users to test functionality
- Consider other servers or devices
- Document findings/lessons, actions, and outcomes
- Full document your research, theories, changes, and updates
- Add information to knowledge base
- Useful if unintended consequences appear
Tech Support Methodologies and Frameworks
What is ITSM?
Implementing ITSM
- Predefined frameworks
- Guides with formalized structure
- Standards, processes, and best practices
Popular ITSM frameworks have these features:
- Strategy
- Design
- Management
- Operation
- Improvement
ITSM Frameworks
ITIL
- Information technology infrastructure library
- Standardized set of detailed practices and processes
- Service strategy
- Service Design
- Service Transition
- Service Operation
- Continual Service Improvement
COBIT and Lean IT frameworks
COBIT
- For governance and management of IT
- Uses processes contained in ITIL
Lean IT
- Framework for applying lean principles to the delivery of IT services
- Designed to cut out waste that doesn’t add value
MOF and ISO/IEC 20000 frameworks
Microsoft Operations Framework
- Guidance for IT lifecycle
- Plan phase
- Deliver phase
- Operate phase
- Manage phase
ISO/IEC 20000
- International standard for ITSM
- Guidelines to establish, implement, operate and maintain
ITSM metrics
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores
- First-contact resolution
- First-level resolution
- Cost per ticket
- Mean time to resolution
Benefits of ITSM processes
- Consistency
- Efficiency
- Management
- Risk and downtime
- Operational costs
- Standardization and accountability
- Higher quality of service
- Improved customer satisfaction
- More agility
ITSM frameworks and technical support
- People are part of ITSM
- Processes based on service
- Standards for managing IT services
- IT solutions and knowledge
- Technical support feedback
Effective Documentation and Communication
Communicating in technical support
- Interest in technology
- Ability to write clearly
- Skills to Communicate
Effective communication
- Informative communication
- Clear explanations
- Faster resolutions
Notes and communication
- Notes
- Word processing
- Spreadsheets
Keep your audience in mind while taking notes or writing documentation and technical abilities and knowledge.
Order of steps
- List what you have tried
- State them chronologically
- State them from most to least important
- Use a clear order
Analysis of the problem
- State what is or is not the problem
- Show how you have worked through the problem
- Include what led to the issue
- Describe what worked in the past but did not this time
- Keep it simple
- Ask clear questions
- Model others
Cheat sheet for Logging a Ticket
- You noted the customer’s name and contact information.
- You included the ticket or issue number and the date the ticket was created.
- You documented the complete details of the problem or issue.
- You noted the priority and urgency of the customer and the issue.
- You logged the issue category, the department, and agent the issue is assigned to.
- You included closing notes.