Software Architecture Design and Patterns
Introduction to Software Architecture
Software architecture and design:
-
Design and documentation take place during the design phase of the SDLC
-
Software architecture is the organization of the system
-
Serves as a blueprint for developers
-
Comprised of fundamentals structures and behaviors
Early design decisions:
-
How components interact
-
Operating environment
-
Design principles
-
Costly to change once implemented
-
Addresses non-functional aspects
Why software architecture is important:
-
Communication
-
Earliest design decisions
-
Flexibility
-
Increases lifespan
Software architecture and tech stacks:
-
Guides technology stack choice
-
Tech stacks must address non-functional capabilities
-
Tech stacks include:
- Software
- Programming languages
- Libs
- Frameworks
- Architects must weigh advantages and disadvantages of tech stack choices
Artifacts
- Software design document (SDD)
- Architectural diagrams
- Unified modeling language (UML) diagrams
- Software Design Document (SDD)
- Collection of tech specs regarding design implementation
- Design considerations:
- Assumptions
- Dependencies
- Constraints
- Requirements
- Objectives
- Methodologies
- Architectural diagrams
It displays:
- Components
- Interactions
- Constraints
- Confines
- Architectural patterns
- UML diagrams
- Visually communicate structures and behaviors
- Not constrained by a programming language
Deployment considerations
- Architecture drives production environment choices
- Production environment is the infrastructure that runs and delivers the software
- Servers
- Load balancers
- Databases
Software Design and Modeling
Software Design:
Software design is a process to document:
-
Structural components
-
Behavioral attributes
Models express software design using:
-
Diagrams and flowcharts
-
Unified Modeling Language (UML)
Characteristics of structured design:
-
Structural elements: modules & submodules
-
Cohesive
-
Loosely coupled
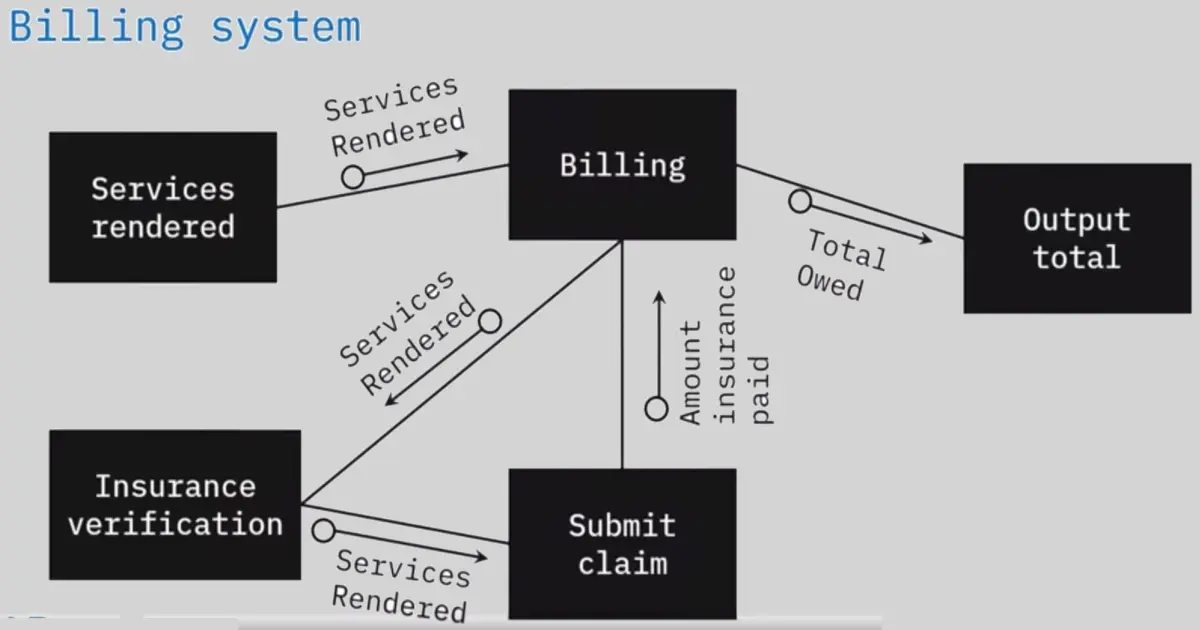
Structure diagram example:
Behavioral models:
- Describe what a system does but doesn’t explain how it does it
- Communicate the behavior of the system
- Many types of behavioral UML diagrams
- State transition
- Interaction
Unified Modeling Language (UML):
- Visual representations to communicate architecture, design, and implementation
- Two types: structural and behavioral
- Programming language agnostic
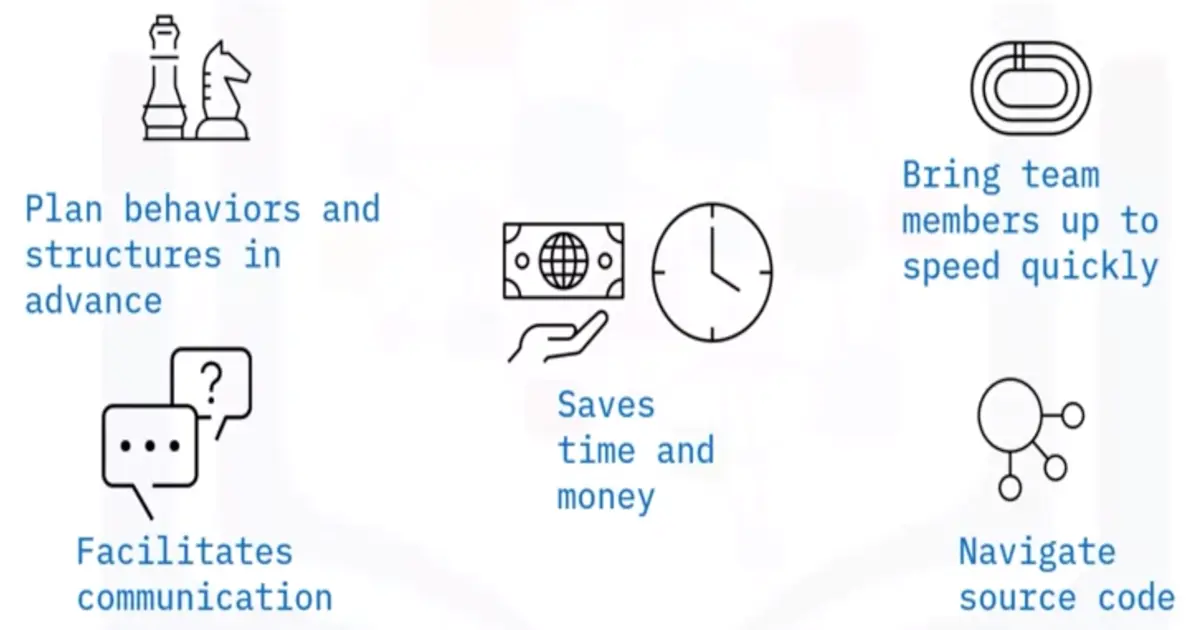
Advantages of Unified Modeling Language (UML):
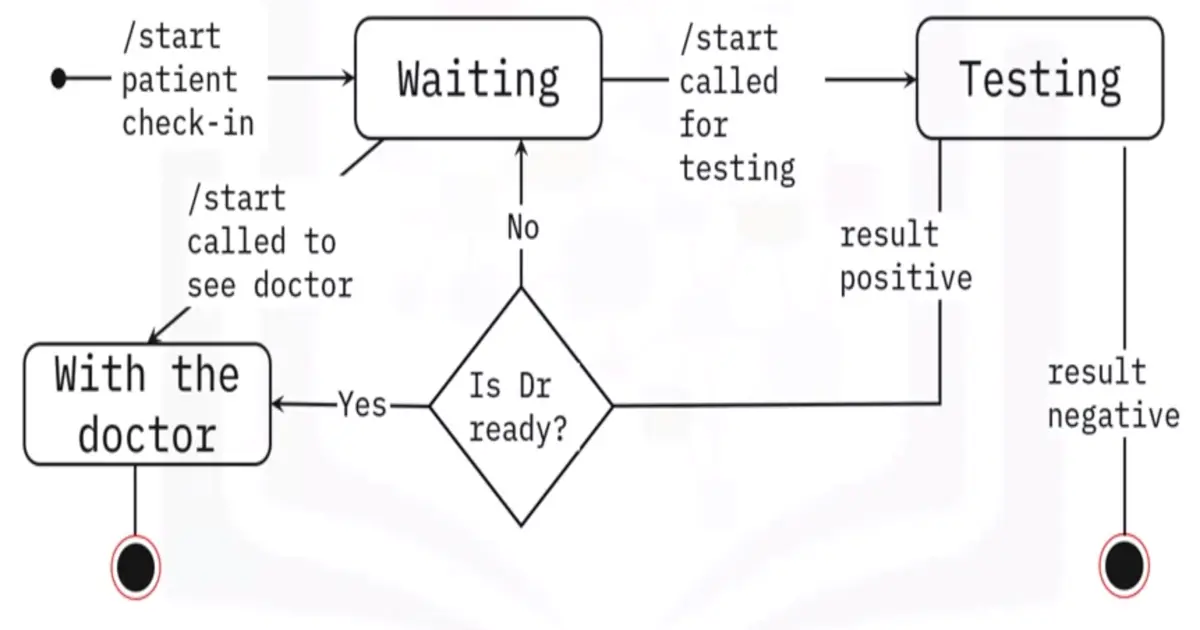
State transition diagram example:
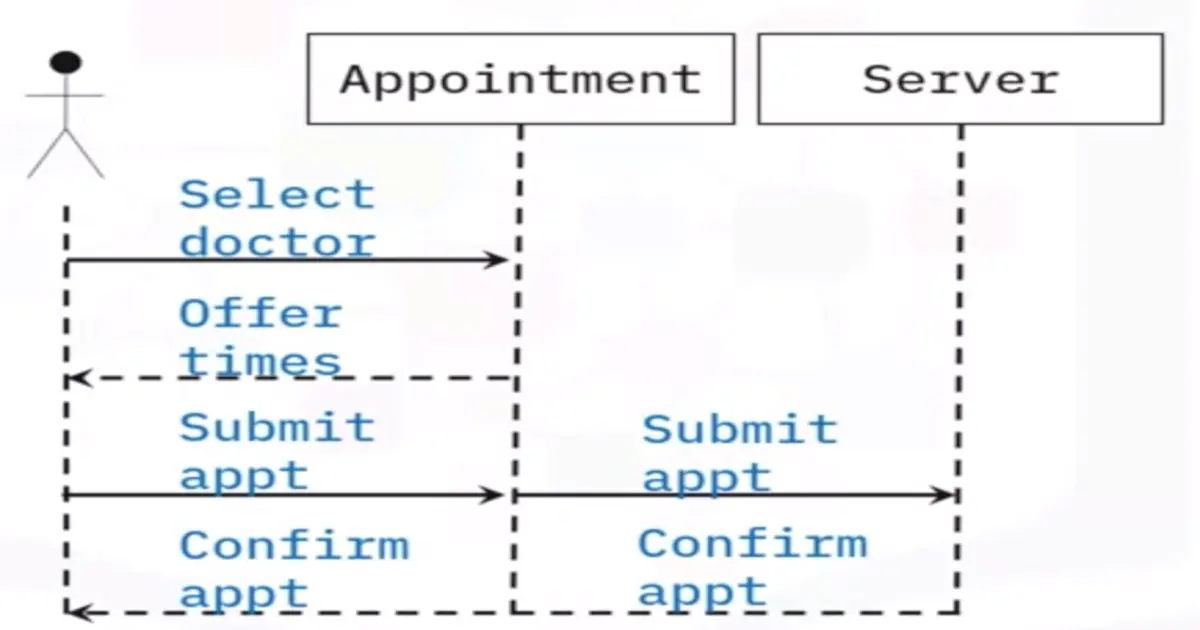
Interaction diagram:
Object-Oriented Analysis and Design
Object-Oriented Languages:
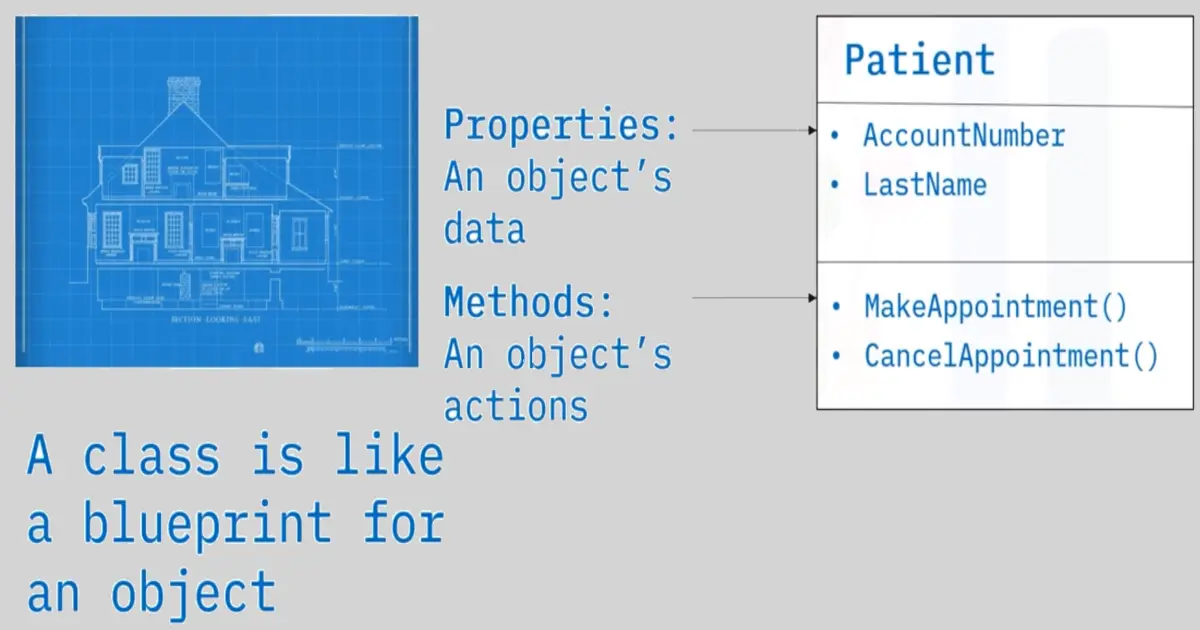
- A patient could be an object
- An object contains data, and an object can perform actions
Classes and objects:
Object-Oriented analysis and design:
- Used for a system that can be modeled by interacting objects
- OOAD allows developers to work on different aspects of the same application at the same time
- Visual UML diagrams can be made to show both static structure and dynamic behavior of a system
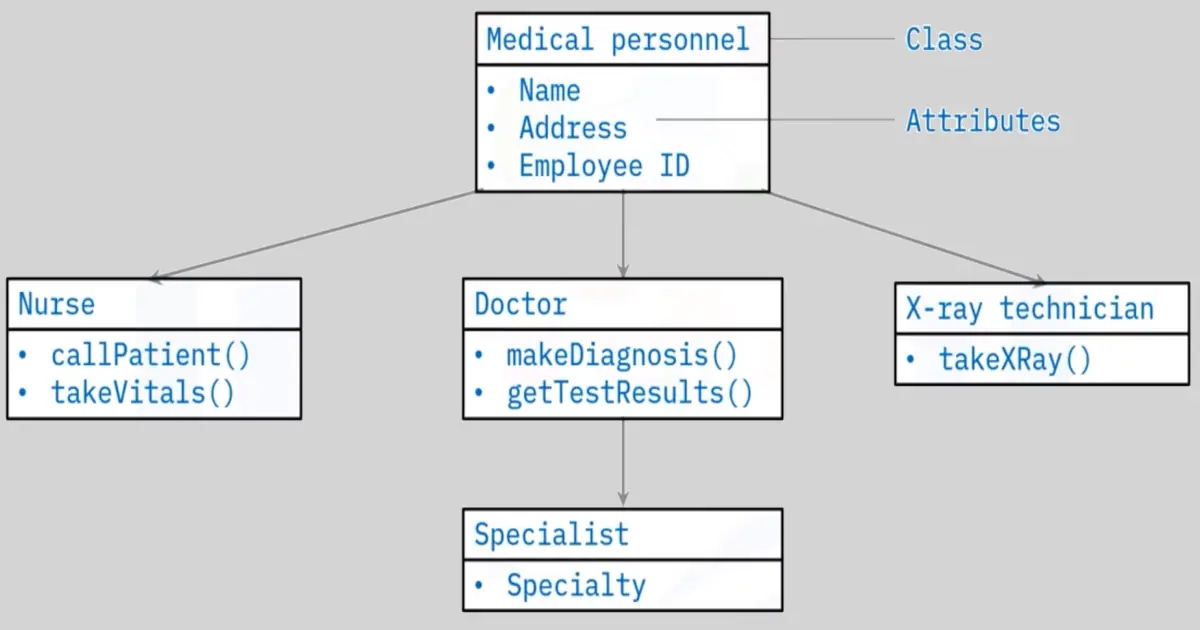
Class diagram:
Software Architecture Patterns and Deployment Topologies
Approaches to Application Architecture
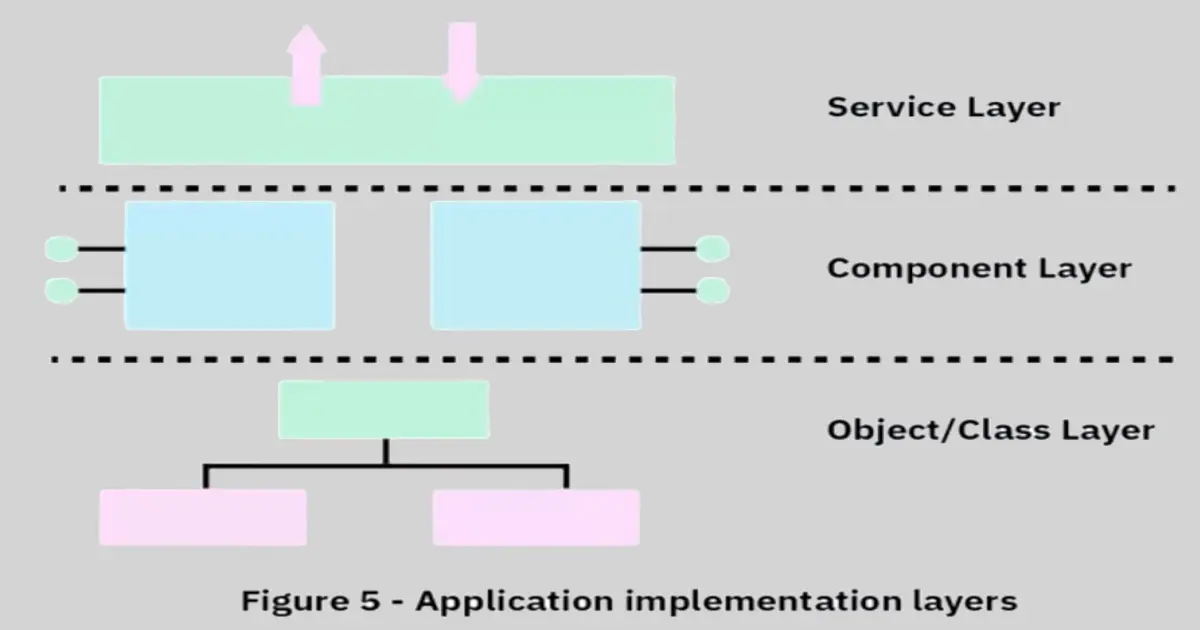
What is component?
- An individual unit of encapsulated functionality
- Serves as a part of an application in conjunction with other components
Component characteristics:
- Reusable: reused in different applications
- Replaceable: easily replaced with another component
- Independent: doesn’t have dependencies on other components
- Extensible: add behavior without changing other components
- Encapsulated: doesn’t expose its specific implementation
- Non-context specific: operates in different environments
Components examples:
Component-based architecture:
- Decomposes design into logical components
- Higher level abstraction than objects
- Defines, composes, and implements loosely coupled independent components, so they work together to create an application
Services
- Designed to be deployed independently and reused by multiple systems
- Solution to a business need
- Has one unique, always running instance with whom multiple clients communicate
Examples of Services:
- A service is a component that can be deployed independently
- Checking a customer’s credit
- Calculating a monthly loan payment
- Processing a mortgage application
Service-oriented architecture:
- Loosely coupled services that communicate over a network
- Supports building distributed systems that deliver services to other applications through the communication protocol
Distributed systems
- Multiple services located on different machines
- Services coordinate interactions via a communication protocol such as HTTP
- Appears to the end-user as a single coherent system
Distributed system characteristics:
- Shares resources
- Fault-tolerant
- Multiple activities run concurrently
- Scalable
- Runs on a variety of computers
- Programmed in a variety of languages
Nodes:
- Any devices on a network that can recognize, process, and transmit data to other nodes on the network
- Distributed systems have multiple interconnected nodes running services
Distributed system architectures:
Architectural Patterns in Software
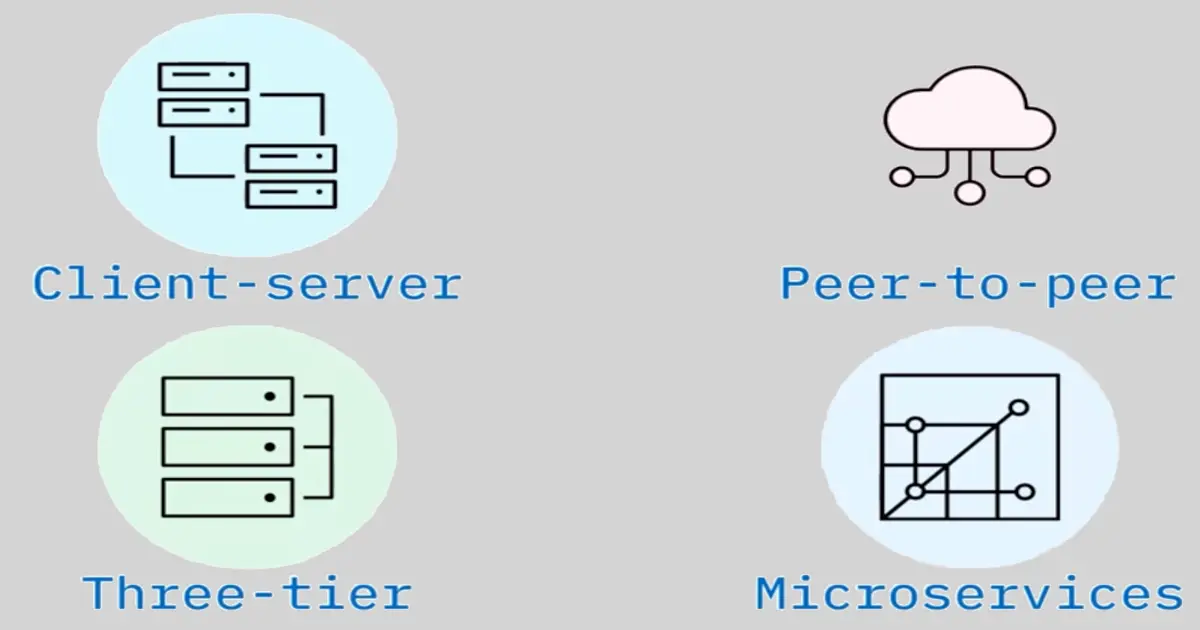
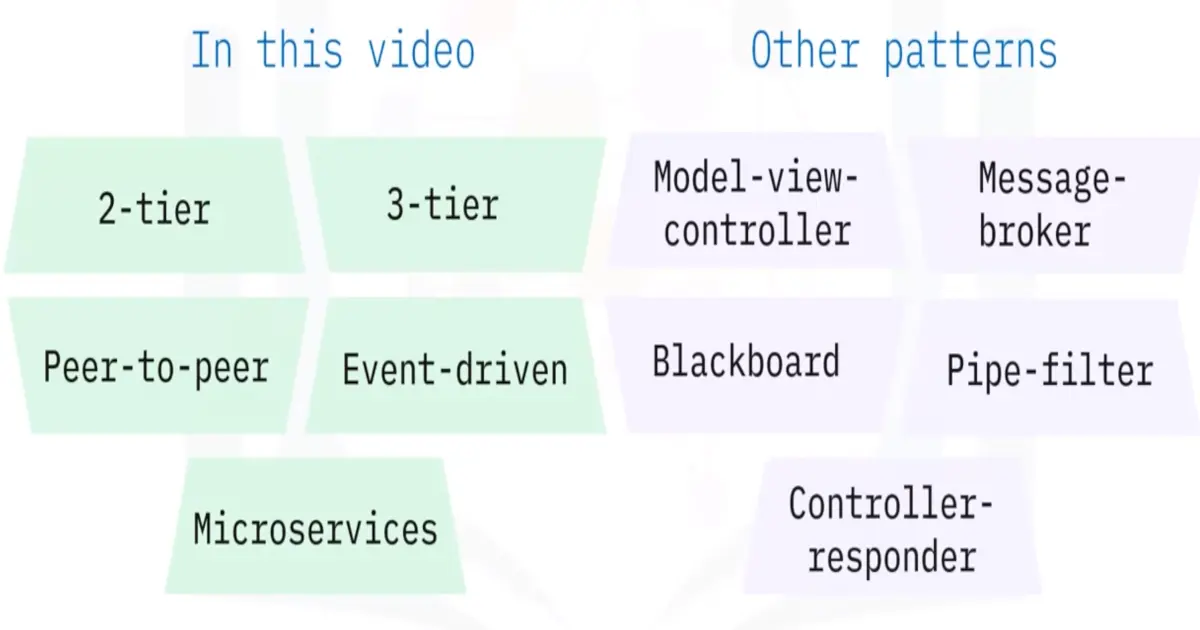
Types of architectural patterns:
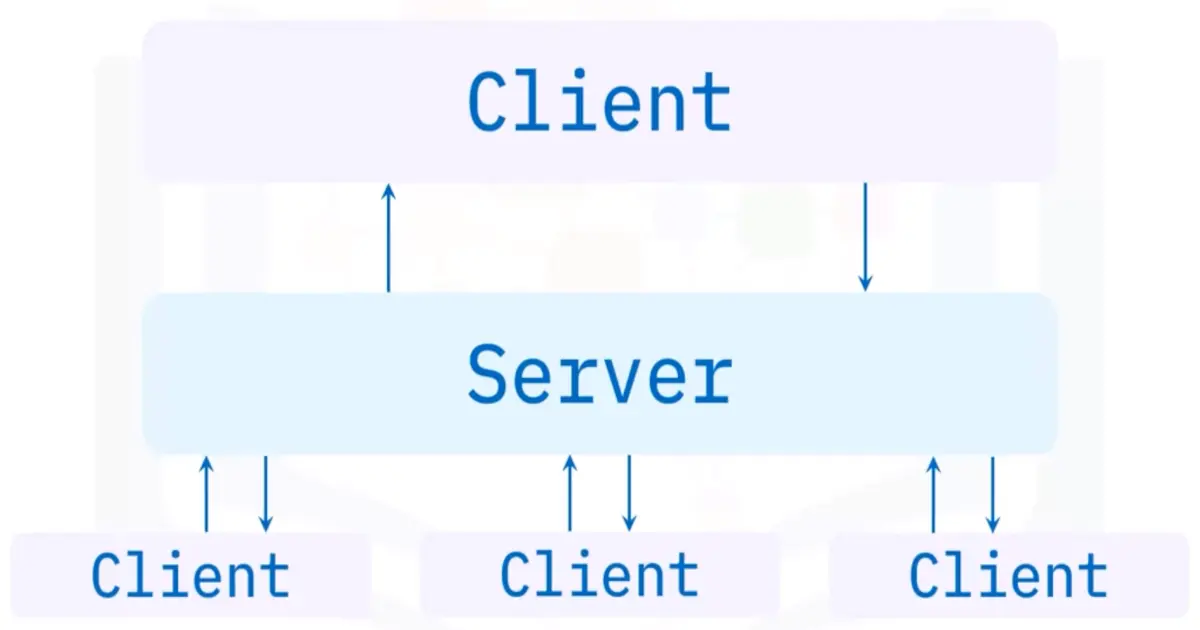
2-tier
3-tier
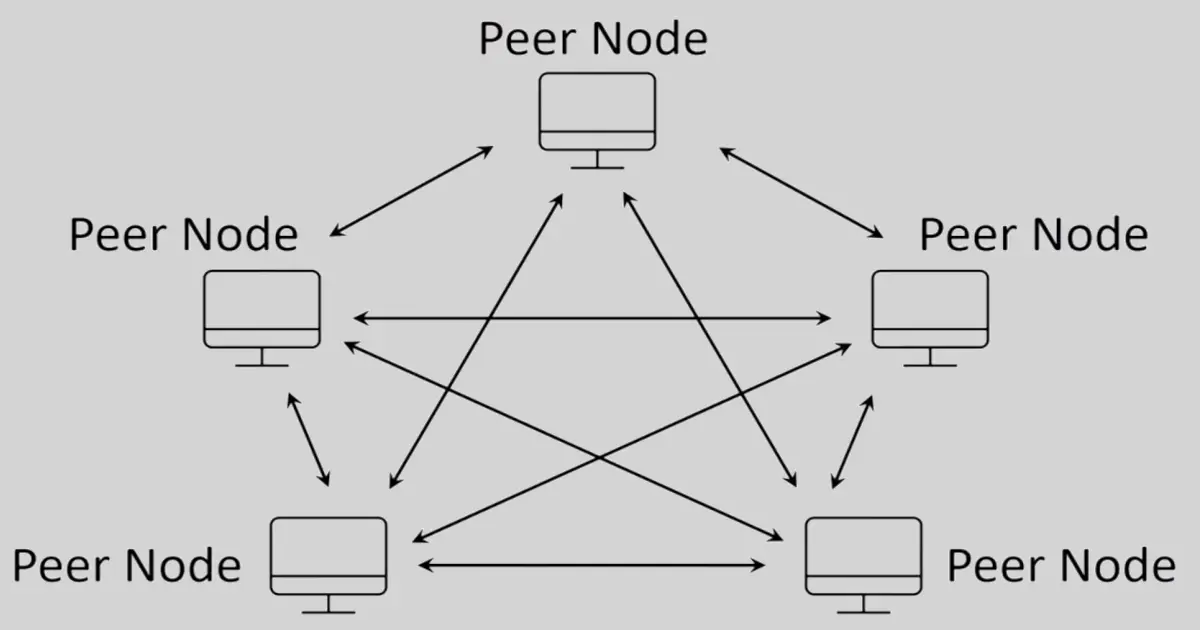
Peer-to-peer (P2P)
Event-driven
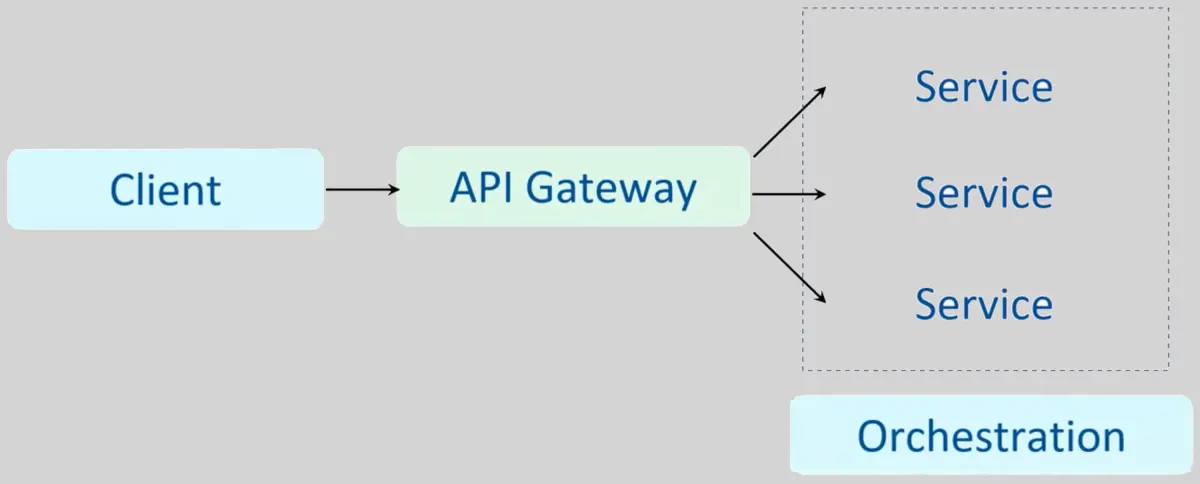
Microservices
Examples:
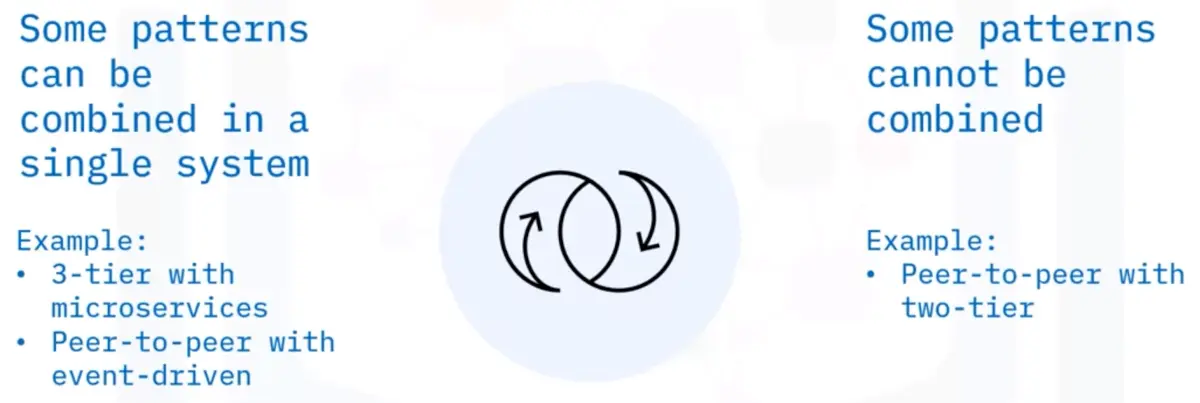
Combining patterns
Application Deployment Environments
Application environments:
Include:
- Application code/executables
- Software stack (libs, apps, middleware, OS)
- Networking infrastructure
- Hardware (compute, memory and storage)
Pre-production environments:
Production environment
-
Entire solution stack ++
-
Intended for all users
-
Take load into consideration
-
Other non-functional requirements
- Security
- Reliability
- Scalability
-
More complex than pre-production environments
On-premises deployment:
-
System and infrastructure reside in-house
-
Offers greater control of the application
-
Organization is responsible for everything
-
Usually more expensive than compared to cloud deployment
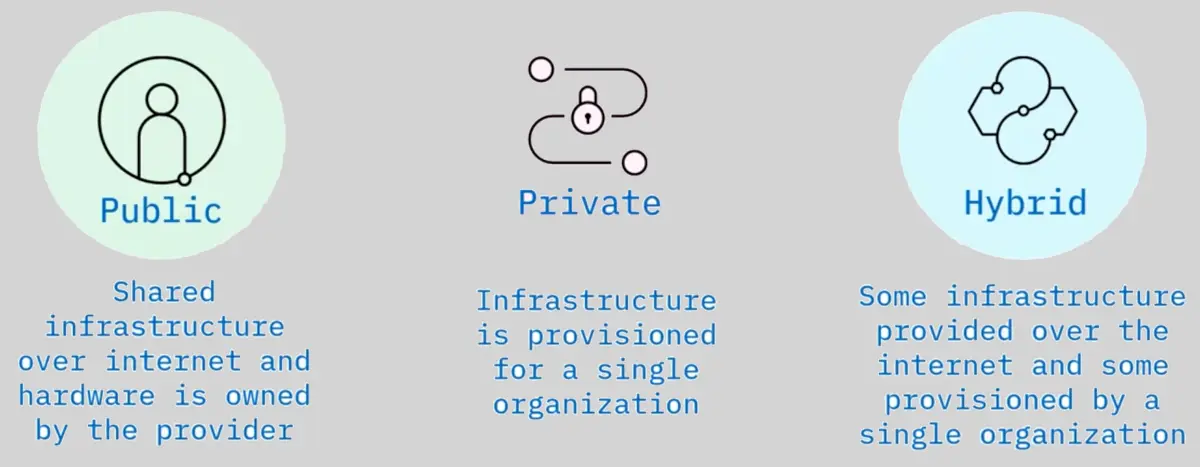
Cloud deployment types:
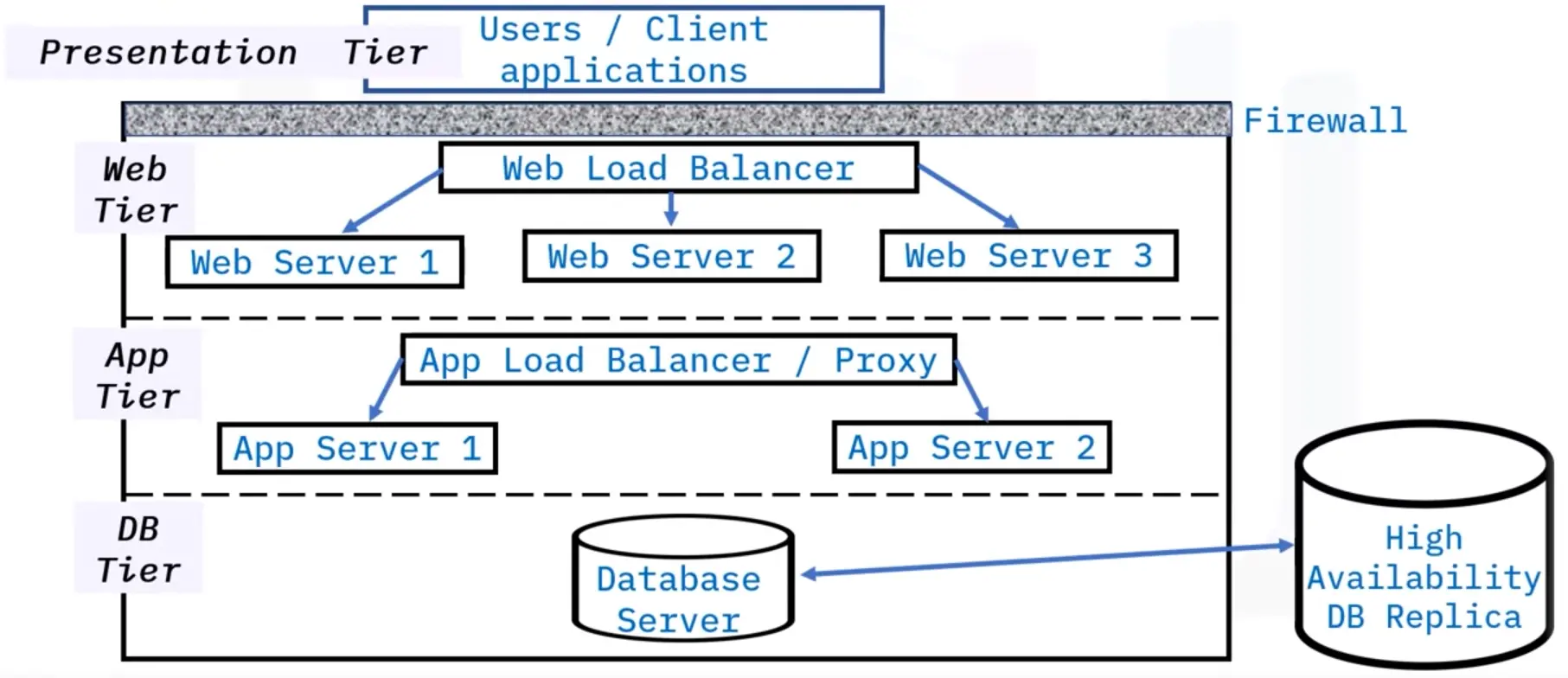
Production Deployment Components
Production deployment infrastructure:
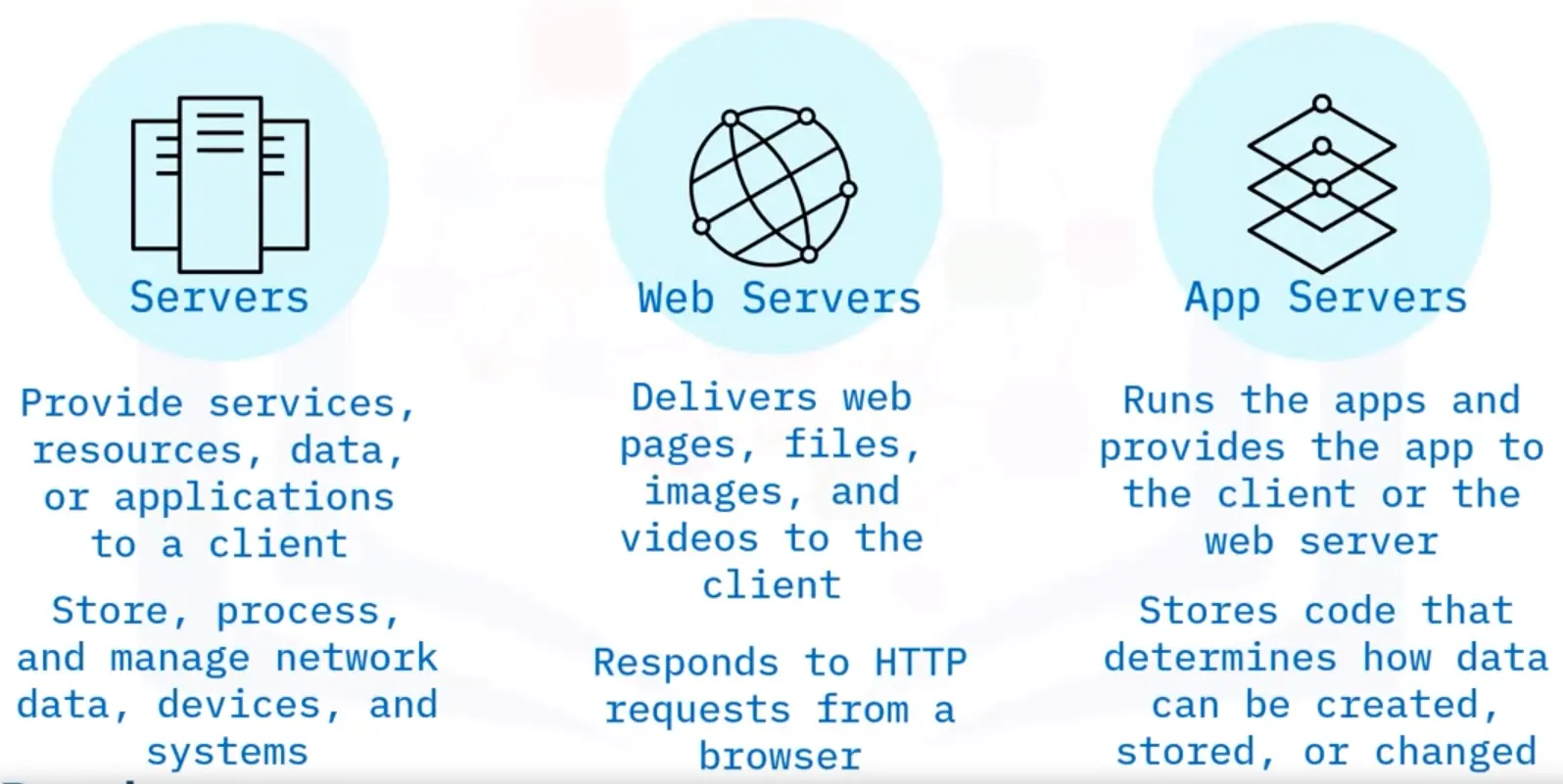
Web and application servers:
Proxy server:
-
An intermediate server that handles requests between two tiers
-
Can be used for load balancing, system optimization, caching, as a firewall, obscuring the source of a request, encrypting messages, scanning for malware, and more
-
Can improve efficiency, privacy, and security
Databases and database servers:
-
Databases are a collection of related data stored on a computer that can be accessed in various ways
-
DBMS (Database Management System) controls a database by connecting it to users or other programs
-
Database servers control the flow and storage of data