Introduction to Shell Scripting
Shell Scripting Basics
What is a script?
-
Script: list of commands interpreted by a scripting language
-
Commands can be entered interactively or listed in a text file
-
Scripting languages are interpreted at runtime
-
Scripting is slower to run, but faster to develop
What is a script used for?
-
Widely used to automate processes
-
ETL jobs, file backups and archiving, system admin
-
Used for application integration, plug-in development, web apps, and many other tasks
Shell scripts and the ‘shebang’
-
Shell script – executable text file with an interpreter directive
-
Aka ‘shebang’ directive
#!interpreter [optional-arg] -
‘interpreter’ – path to an executable program
-
‘optional-arg’ – single argument string
Example – ‘shebang’ directives
Shell script directive:
#!/bin/sh
#!/bin/bashPython script directive:
#!/usr/bin/env python3Filters, Pipes, and Variables
Pipes and filters:
Filters are shell commands, which:
-
Take input from standard input
-
Send output to standard output
-
Transform input data into output data
-
Examples are
wc, cat, more, head, sort, … -
Filters can be chained together
Pipe command –
| -
For chaining filter commands
commmand1 | command2 -
Output of command 1 is input of command 2
-
Pipe stands for pipeline
Shell variables:
-
Scope limited to shell
-
Set– list all shell variablesDefining shell variables:
var_name=value -
No spaces around
=unset var_name -
deletes
var_name
Environment Variables:
-
Extended scope
export var_name -
env— list all environment variables
Useful Features of the Bash Shell
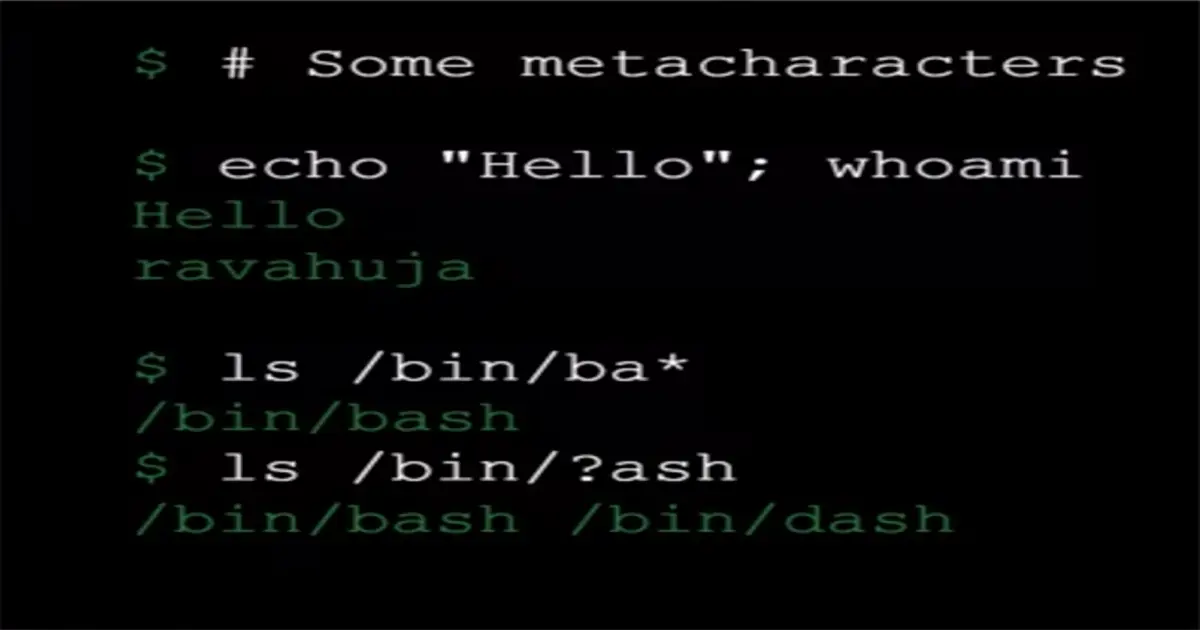
Metacharacters
#— precedes a comment;— command separator*— filename expansion wildcard?— single character wildcard in filename expansion
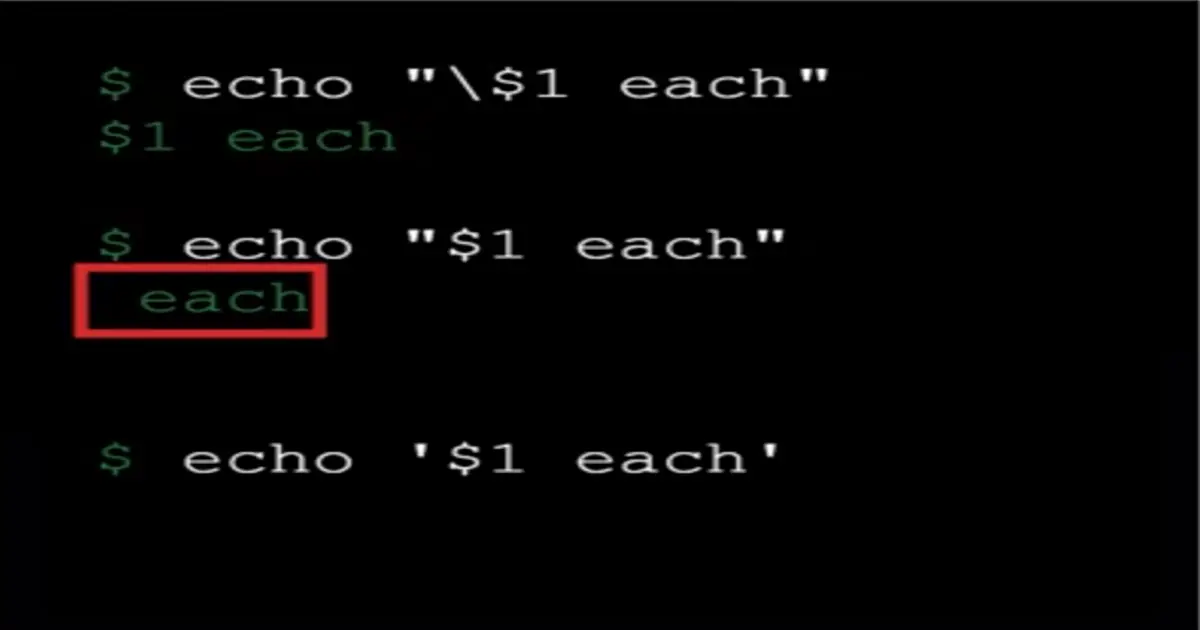
Quoting
\— escape special character interpretation""— interpret literally, but evaluate meta-characters''— interpret literally
I/O redirection
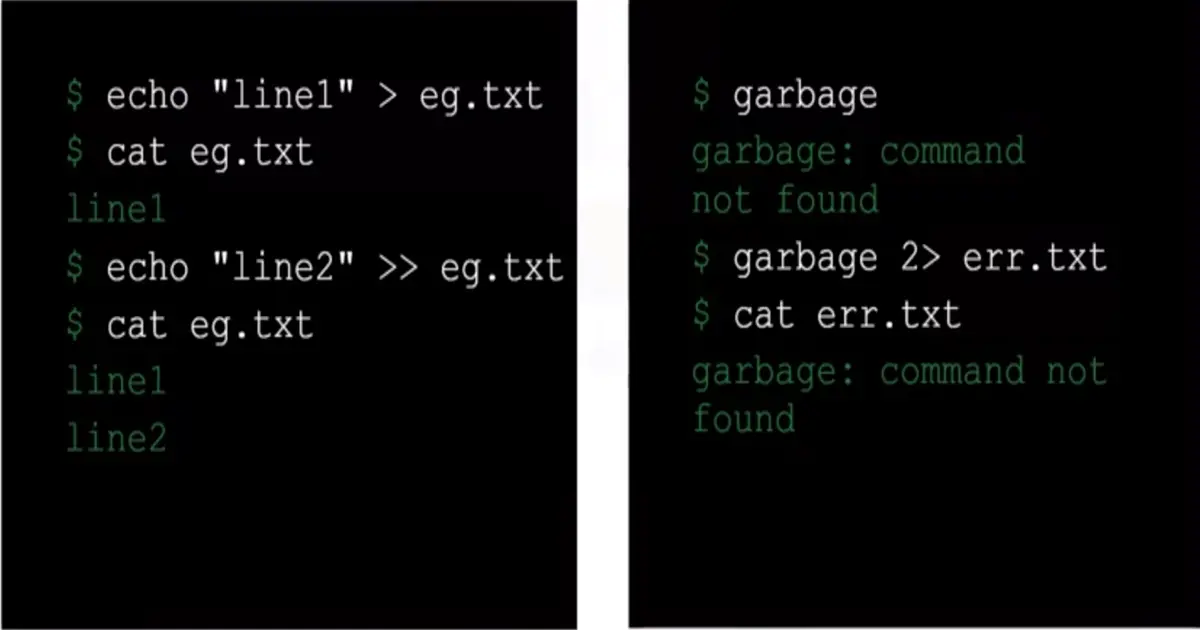
Input/Output, or I/O redirection, refers to a set of features used for redirecting
>— Redirect output to file>>— Append output to a file2>— Redirect standard error to a file2>>— Append standard error to a file<— Redirect file contents to standard input
Command substitution
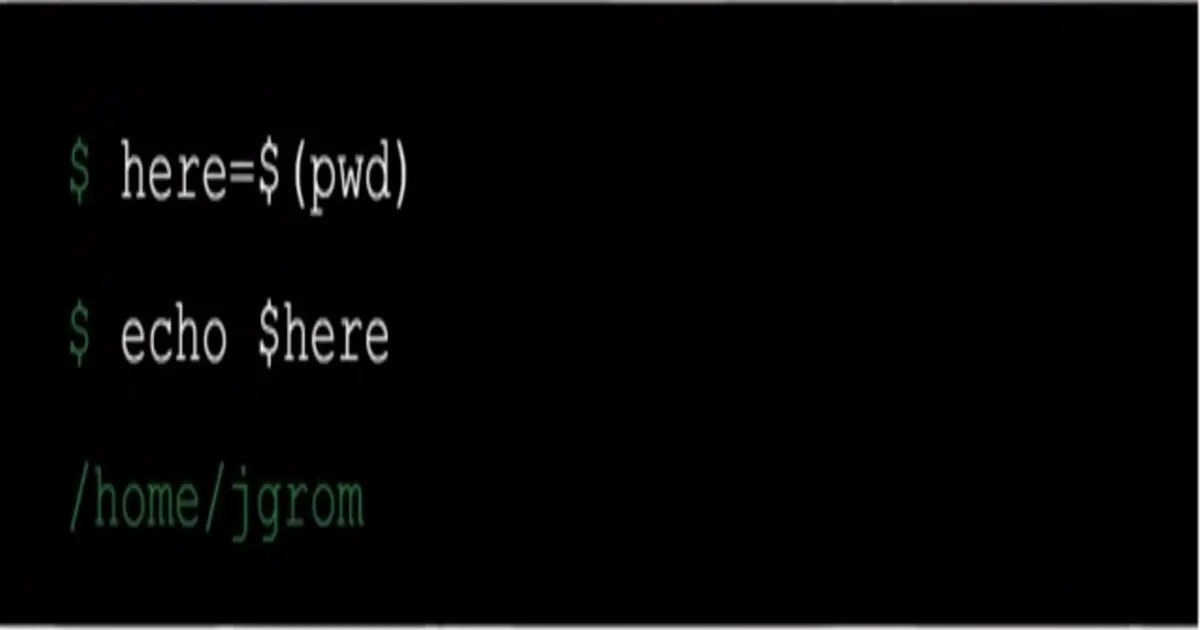
-
Replace command with its output
$(command) or `command` -
Store output of
pwdcommand inhere:
Command line arguments
-
Program arguments specified on the command line
-
A way to pass arguments to a shell script
./MyBashScript.sh arg1 arg2
Batch vs. concurrent modes
Bath mode:
-
Commands run sequentially
command1; command2Concurrent mode:
-
Commands run in parallel
command1 & command2
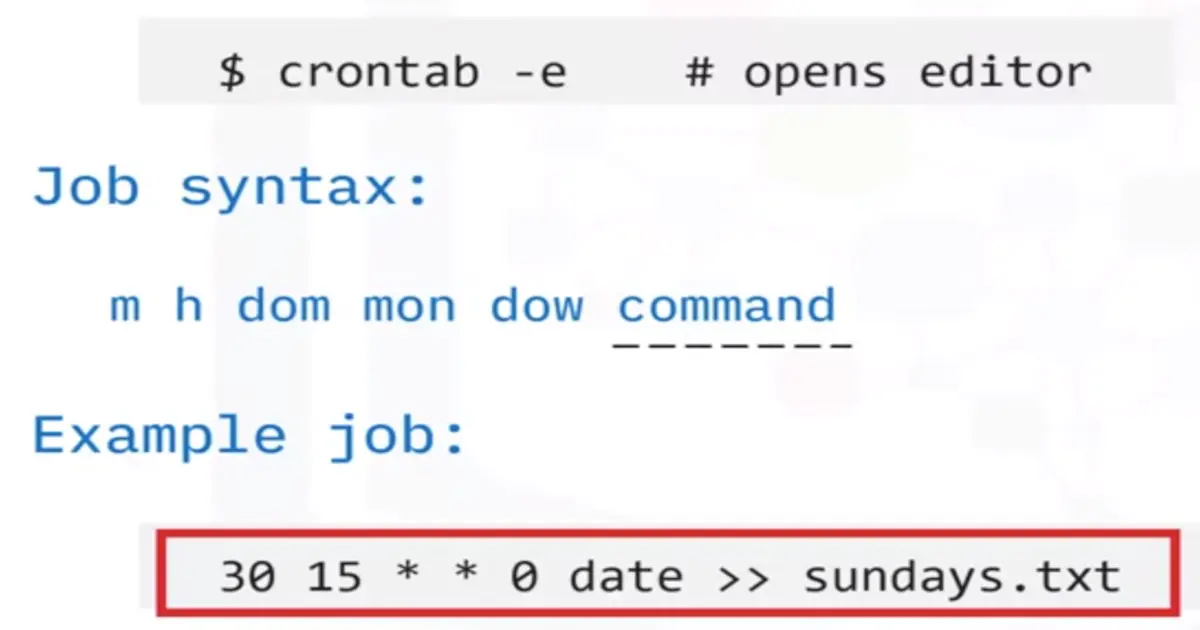
Scheduling Jobs using Cron
Job scheduling
-
Schedule jobs to run automatically at certain times
- Load script at midnight every night
- Backup script to run every Sunday at 2 AM
-
Cron allows you to automate such tasks
What are cron, crond, and crontab?
-
Cron is a service that runs jobs
-
Crond interprets ‘crontab files’ and submits jobs to cron
-
A crontab is a table of jobs and schedule data
-
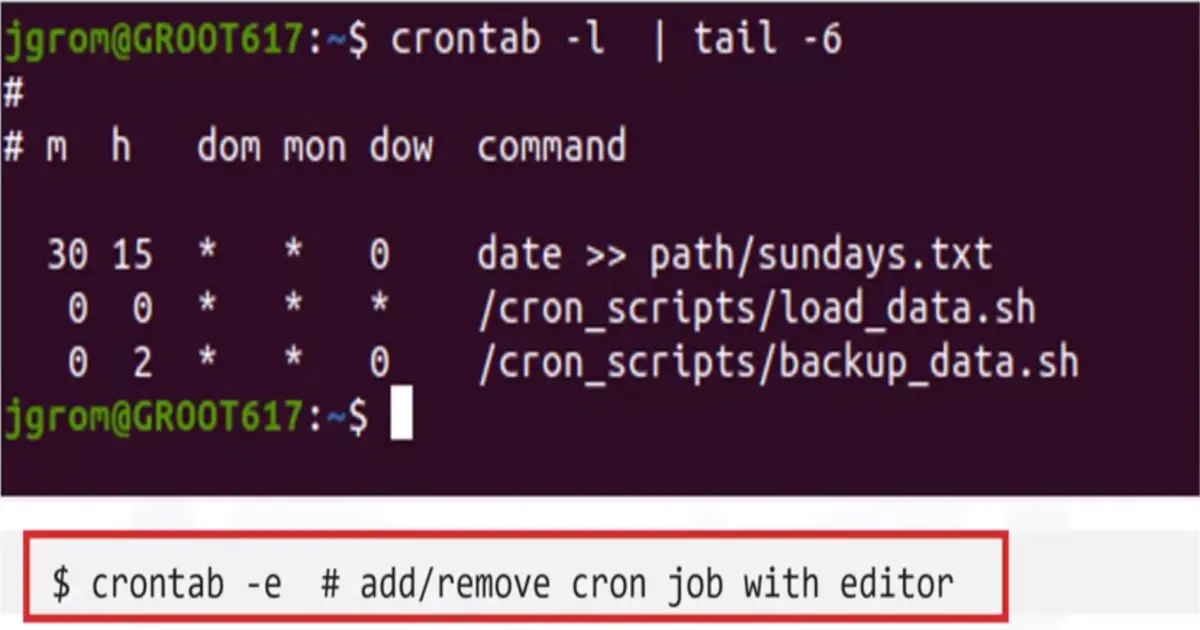
Crontab command invokes text editor to edit a crontab file
Scheduling cron jobs with crontab
Viewing and Removing cron jobs